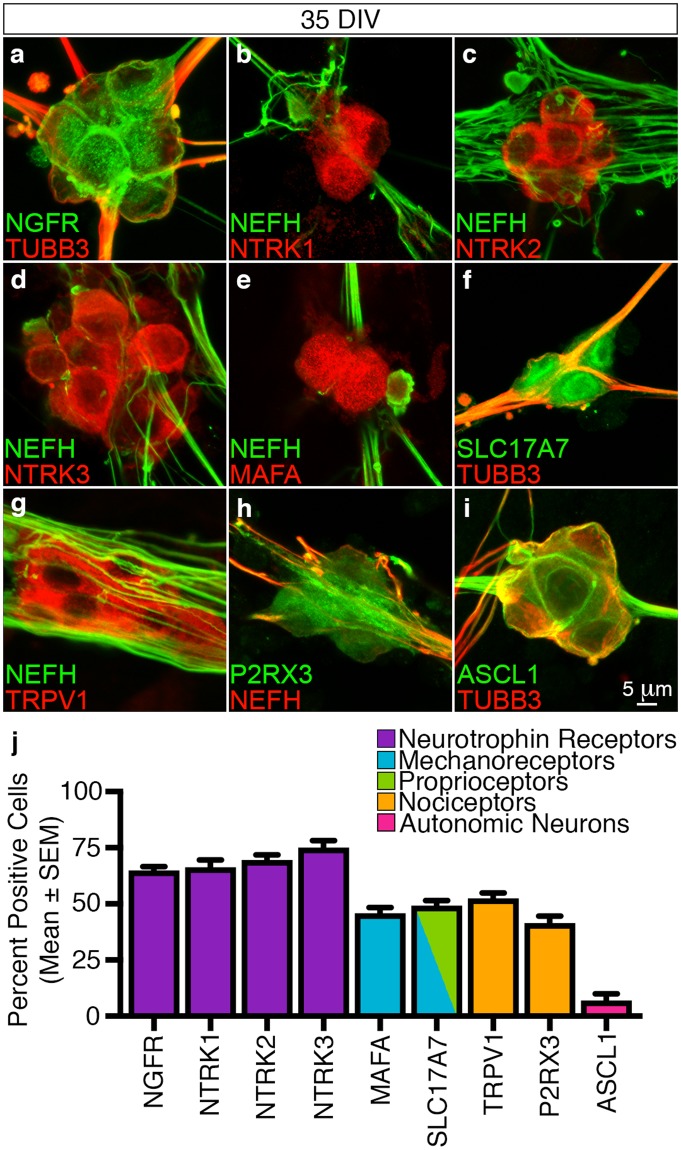
Figure 3.
Molecular subtype characterisation of in vitro differentiated peripheral sensory neurons. Differentiated peripheral sensory neurons were characterised using combinations of subtype-specific markers at 35 DIV. (a–d) The differentiated peripheral sensory neurons express NGFR and all three NTRK family members (NTRK1, NTRK2 and NTRK3) thus confirming that the in vitro cultures are comprised of mechanoreceptive, nociceptive and proprioceptive subtypes. (e–h) Combinatorial expression of axonal (NEFH and TUBB3) with subtype-specific markers (MAFA, SC17A7, TRPV1 and P2RX3) demonstrates that the differentiated peripheral sensory neurons express marker permutations that are the molecular hallmarks of mechanoreceptors (NEFH+/MAFA+ and TUBB3+/SLC17A7+), proprioceptors (TUBB3+/SCL17A7+) and nociceptors (NEFH+/TRPV1+ and NEFH+/P2RX3+). (i) A small minority of neuronal ganglia were also determined to be ASCL1+ suggesting that some cells generated during the differentiation protocol were autonomic neurons. Additional overview images are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1. (j) Quantitative analyses (mean ± SEM) of neuronal ganglia at 35 DIV illustrate the molecular heterogeneity of the in vitro differentiated sensory neurons. All images and quantification analyses were performed on neurons derived from at least three independent differentiation experiments. Abbreviations: DIV, days in vitro. Scale bars: (a–i) 5 μm.