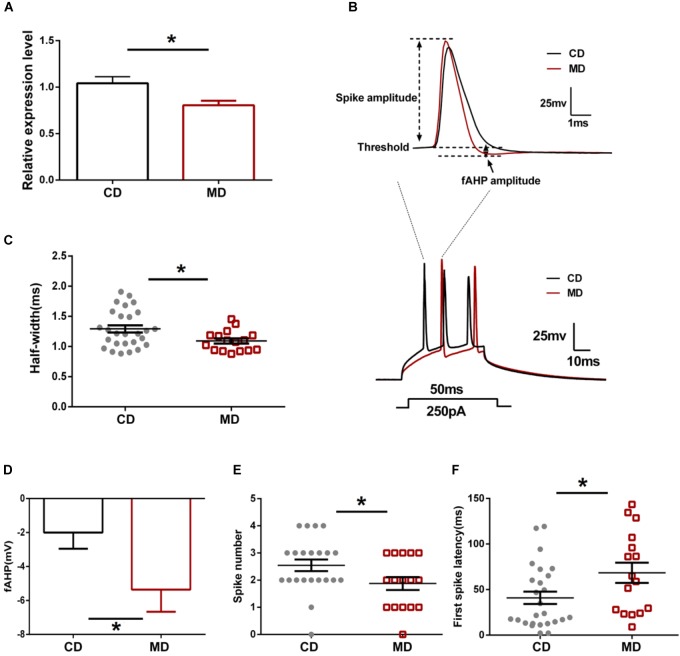
FIGURE 1.
Different intrinsic excitability of CA1 pyramidal neurons in the MD F1 mice compared to the CD F1 mice. (A) qRT-PCR showing reduced expression of Kcnmb2 in the hippocampus of MD F1 mice. Unpaired t-test, n = 5 mice for each group. (B) Sample recordings showing action potentials evoked by a depolarizing current injection. Upper: the first spike in response to a current injection (250 pA, 50 ms) into CA1 pyramidal neurons of CD F1 mice (black trace) and MD F1 mice (red trace). Lower: spikes trains evoked by a depolarizing current injection (250 pA, 50 ms) into CA1 pyramidal neurons of MD F1 (red trace) and CD F1 (black trace) mice. (C) Reduced action potential half-width in CA1 pyramidal neurons of MD F1 mice compared to CD F1 controls. Unpaired t-test, n = 27 cells from six CD F1 mice and n = 16 cells from five MD F1 mice. (D) Increased peak fAHP in CA1 pyramidal neurons of MD F1 mice. Unpaired t-test, n = 27 cells from six CD F1 mice and n = 17 cells from five MD F1 mice. (E) Reduced spike number in CA1 pyramidal neurons of MD F1 mice. Unpaired t-test, n = 22 cells from six CD F1 mice and n = 16 cells from five MD F1 mice. In (C–E), depolarizing current was 250 pA and 50 ms in duration. (F) Prolonged latency to first spike in CA1 pyramidal neurons of MD F1 mice. Depolarizing current was 150 pA and 600 ms in duration. Unpaired t-test, n = 26 cells from six CD F1 mice and n = 16 cells from five MD F1 mice. ∗P < 0.05 means significant difference. All data are shown as means ± SEM.