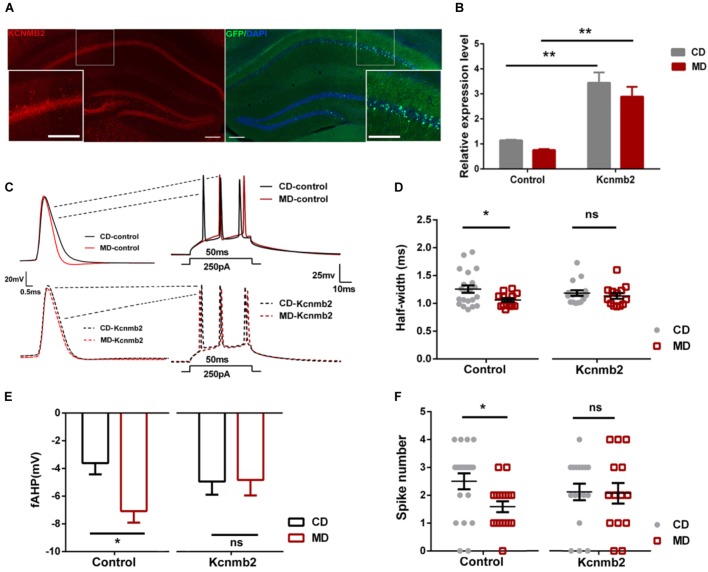
FIGURE 3.
Overexpression of Kcnmb2 in the hippocampus masked MD-F1-associated alterations in intrinsic excitability of CA1 pyramidal neurons (A) Representative images showing AAV-associated GFP (right) and Kcnmb2 expression (left) in dorsal hippocampus. Red, green, and blue fluorescence reflects Kcnmb2-, GFP-, and DAPI-associated signal, respectively. Scale bars represent 100 μm. The insets are higher magnification images of the boxed area. (B) Quantification of the relative Kcnmb2 mRNA expression in the hippocampus after delivery of AAV-Kcnmb2 or AAV-control virus into CA1 region of MD and CD F1 mice. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, n = 4, 4, 6, and 6 samples for CD-control, MD-control, CD-Kcnmb2, and MD-Kcnmb2 groups, respectively. (C) Sample recordings in virus-infected CA1 pyramidal neurons (GFP+) showing action potentials evoked by a depolarizing current injection in CD and MD F1 mice. Left: the first spike in response to a current injection (250 pA, 50 ms) into CA1 pyramidal neuron. Right: spikes trains evoked by a depolarizing current injection (250 pA, 50 ms) into CA1 pyramidal neurons. CD F1 neuron (black) and MD F1 neuron (red) infected by AAV-control (solid traces) or AAV-Kcnmb2 (dashed traces) virus. Comparisons of action potential half-width (D), fAHP (E), and spike numbers (F) between CD and MD F1 neurons infected by control or Kcnmb2 virus. Two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, 5–6 mice per group. AP half-width: n = 21 cells for CD-control, n = 13 cells for MD-control, n = 16 cells for CD-Kcnmb2 and n = 13 cells for MD-Kcnmb2; fAHP: n = 14 cells for CD-control, n = 15 cells for MD-control, n = 16 cells for CD-Kcnmb2 and n = 14 cells for MD-Kcnmb2; Spike number: n = 20 cells for CD-control, n = 17 cells for MD-control, n = 17 cells for CD-Kcnmb2 and n = 14 cells for MD-Kcnmb2. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.01 means significant difference, ns means not significant. All data are shown as means ± SEM.