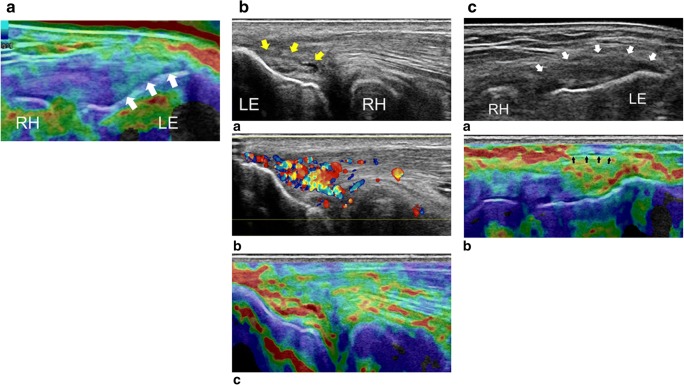
Fig. 5.
CE in the evaluation of the common tendon of the lateral epicondyle. a USE image of the common extensor tendon in the longitudinal plane in a healthy individual. The tendon insertion is shown to have a rigid homogeneous structure (arrows). b (a) The B-mode conventional US image of the extensor tendon in the longitudinal plane. High-grade tendinosis is seen with fibre dehiscence (yellow arrows). At the same level, Doppler (b) demonstrates hypervascularisation and the elastogram (c) shows pathological decrease of the common extensor tendon stiffness. c (a) B-mode conventional US image of the common extensor tendon in the longitudinal plane demonstrating bulging and thickening of the insertion (white arrows). At the same level, the elastogram (b) shows irregular stiffness, involving the peritendinous fascia (black arrows), with pathological adhesion between the tendon and the surrounding tissue. LE: lateral epicondyle, RH: radiohead. Reproduced, with permission, from Klauser et al. [26], copyright (2014) by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (RSNA)