Figure 1: Sites of Action for Antiplatelet Agents.
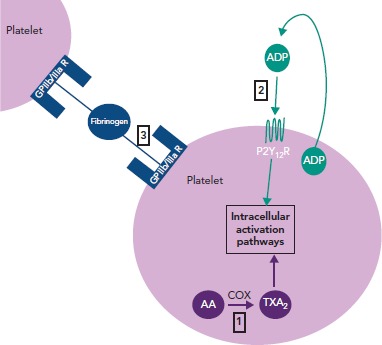
This figure shows the pathways that are interrupted by antiplatelet drugs to impair platelet activation and aggregation. 1: Aspirin acts to inhibit the activity of the cyclooxygenase enzyme and thus attenuates the production of prostaglandins and thromboxane. 2: The ADP receptor antagonists bind to the P2Y12 receptor to prevent ADP-induced platelet activation. 3: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors impair platelet adhesion by preventing the formation of fibrinogen bridges between platelets. AA = arachidonic acid; ADP = adenosine diphosphate; COX = cyclooxygenase; GP = glycoprotein; TXA2 = thromboxane A2.
