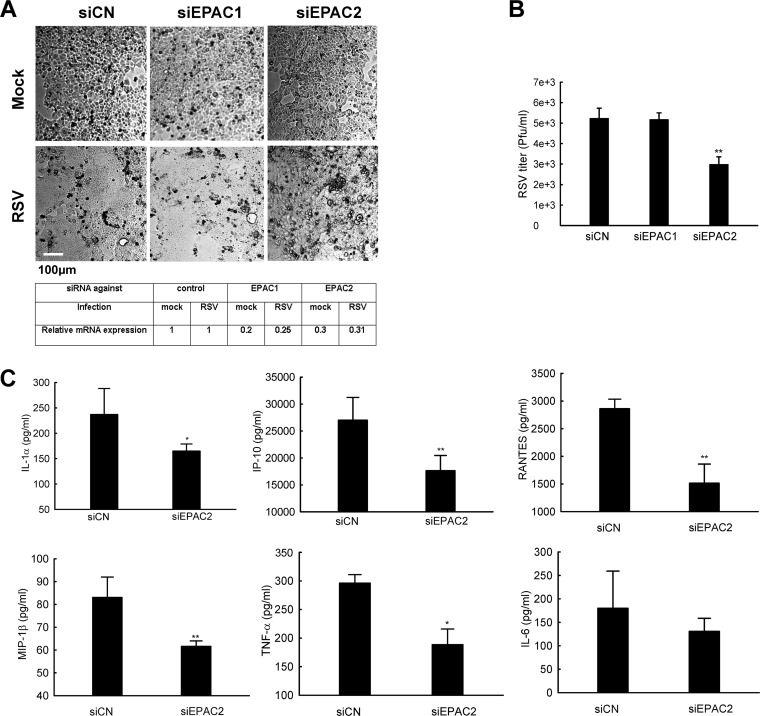
FIG 6.
EPAC2 affects RSV-induced fusion in RPMI 2650 cells. (A) The impact of EPAC isoforms on RSV syncytium formation. RPMI 2650 cells were treated with siRNAs and infected with viruses as described for Fig. 4. The impact of EPAC isoforms on syncytium formation was investigated through a phase-contrast microscope. Total RNA extracts were also prepared for qRT-PCR to confirm gene suppression by siRNAs as indicated. (B) The role of EPAC isoforms in RSV replication. Total viruses, harvested from RPMI 2650 cells (12-well plate), were titrated in HEp-2 cells using immunostaining. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments and means ± SE. *, P < 0.05 relative to the siCN. (C) The regulatory function of EPAC isoform in host innate responses to RSV. Supernatants were harvested from the cells shown in panel A, and the net induction of cytokines/chemokines by RSV infection was measured by Bio-Plex. Data are representative of three independent experiments and are expressed as mean ± SE normalized luciferase activity. P < 0.05 (*) and P < 0.01 (**) relative to the siCN-treated and RSV-infected group.