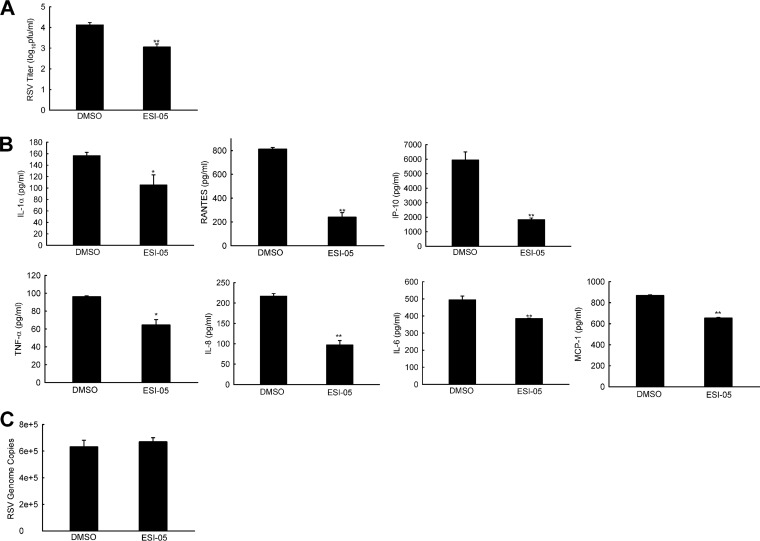
FIG 8.
Role of ESI-05 in RSV replication and RSV-induced innate immunity. (A) Viral replication regulation by ESI-05. SAE cells were mock infected or infected with RSV at an MOI of 1. At 2 h p.i., the cells were washed with PBS, followed by ESI-05 treatment. At 15 h p.i., the total viruses were harvested and titrated. DMSO was used as a vehicle control for ESI-05. (B) The effect of ESI-05 on RSV-induced host innate immunity. SAE cells were infected with RSV at an MOI of 5, followed by ESI-5 treatment at 2 h p.i. At 4 h p.i., the supernatants were harvested, followed by Bio-Plex analysis to investigate the impact of ESI-05 on the induction of cytokines/chemokines by RSV. (C) The samples, after the removal of supernatant, were harvested for total RNA preparation, followed by RT-PCR to quantify the RSV genome. The net induction of proinflammatory mediators and viral genome data are representative of three independent experiments. P < 0.05 (*) and P < 0.01 (**) relative to the DMSO-treated RSV-infected group.