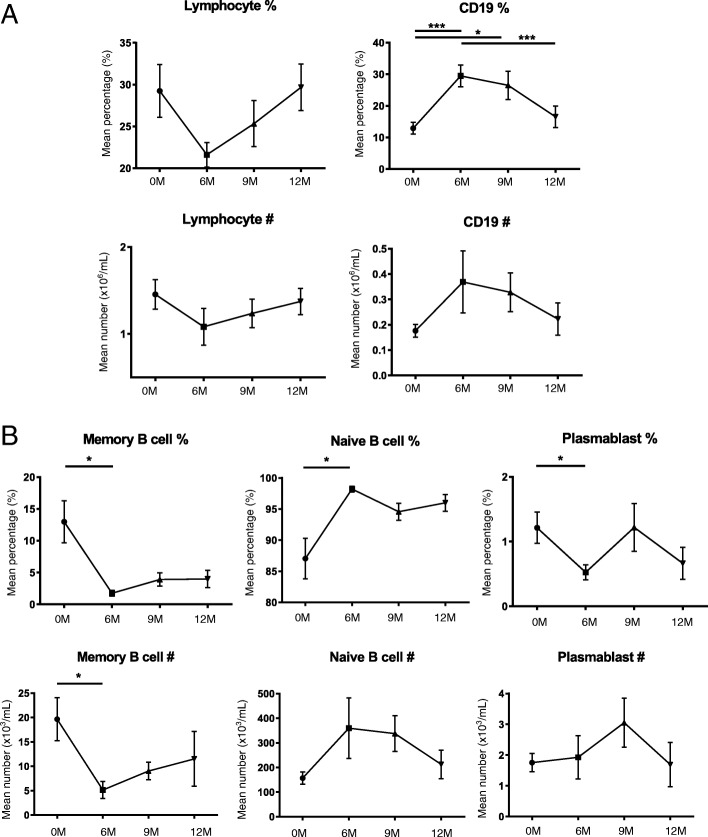
Fig. 3.
Naive B cells predominate repopulated CD19+ cells following alemtuzumab treatment. In order to evaluate the B cell subset distribution post-alemtuzuamb, thawed PBMCs of alemtuzumab-treated patients (n = 11) were evaluated up to 12 months after induction. a Cumulative data for the frequency and the absolute number of total lymphocytes and CD19+ B cells. Successful depletion and reconstitution of lymphocytes and CD19+ B cells was confirmed. b Cumulative data for the frequency and the absolute number of CD19+CD27+ memory B cells, CD19+CD27− naïve B cells, and CD19+CD27+CD38hi plasmablasts. Following alemtuzumab, significant reduction in the frequency of memory B cells (6 M vs 0 M: p = 0.0278) and plasmablasts (6 M vs 0 M: p = 0.0448) was observed and dominance of naïve B cells was observed (6 M vs 0 M: p = 0.0269). The absolute number of memory B cells was significantly decreased compared to 0 M (6 M vs 0 M: p = 0.0112). All values show mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed by repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc analysis