Fig. 4.
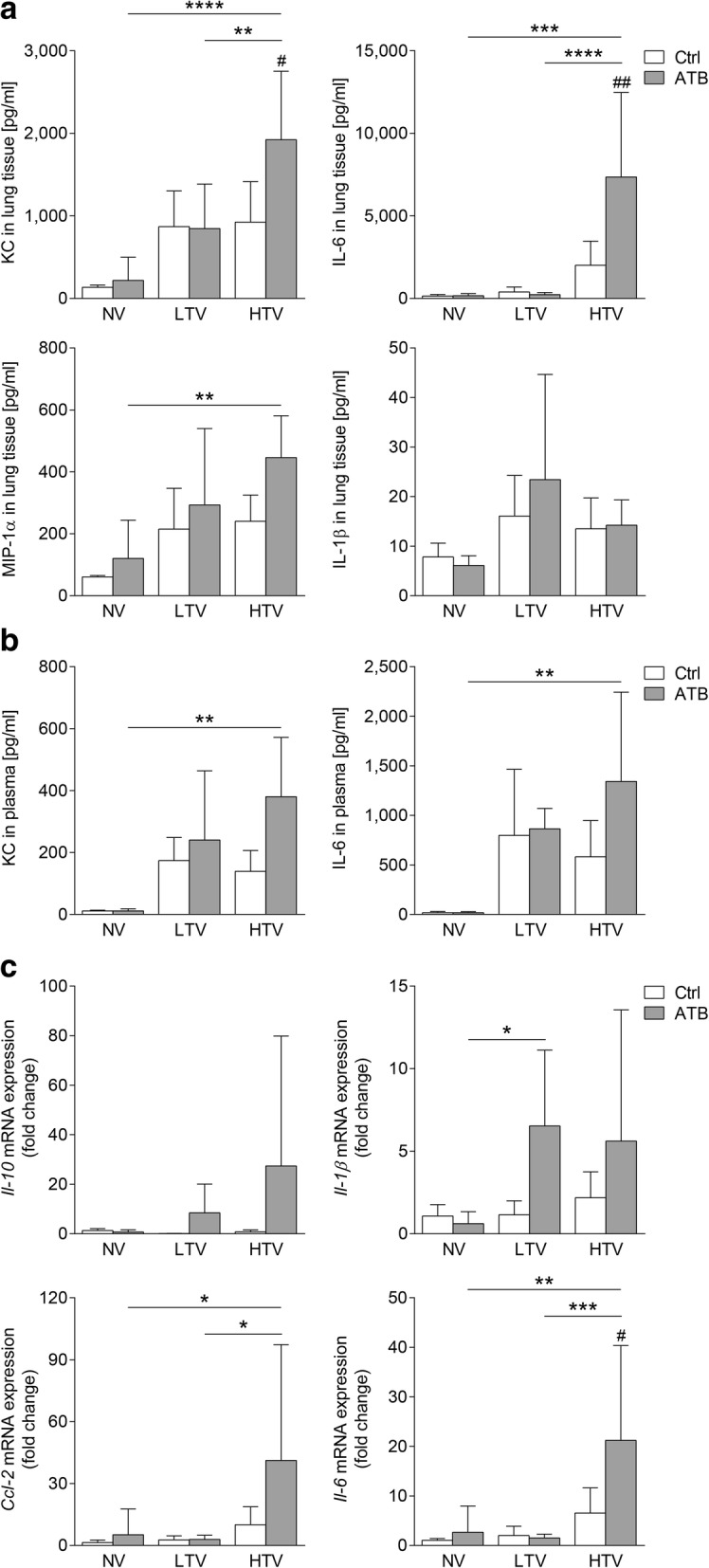
Microbiota depletion prior to mechanical ventilation aggravated the inflammatory response in ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI). Mice received antibiotic broad-spectrum therapy (ATB). Control (Ctrl) mice did not receive antibiotic treatment. VILI was induced 3 days after completing antibiotic treatment protocol by high tidal volume (HTV) ventilation (34 ml/kg; positive end-expiratory pressure = 2 cmH2O, 4 h). Additional groups of mice were ventilated with low tidal volume (LTV) or did not receive ventilation (NV). Keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC), macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α), IL1β and IL-6 protein levels were measured in lung homogenates (a) and in plasma (b) (KC and IL-6) using multiplex assays. c mRNA expression levels of Il-6, Il-10, Ccl-2 and Il-1β were measured by qPCR, normalized to Gapdh levels and related to the average expression of the target gene in NV control mice as described previously [25]. Values are given as mean and SD. In a n = 8 (HTV ctrl), n = 7–8 (LTV ctrl), n = 7 (HTV ATB, LTV ATB), n = 5 (NV ATB), or n = 4 (NV ctrl); in b n = 6–8 (HTV ATB), n = 6–7 (LTV ctrl, HTV ctrl), n = 5 (NV ATB), n = 4–7 (LTV ATB), or n = 3 (NV ctrl); in c n = 8 (NV ATB), n = 6–7 (NV ctrl), n = 3–8 (LTV ctrl), n = 3–7 (HTV ctrl), n = 2–7 (LTV ATB), or n = 5–6 (HTV ATB). Analysis was by two-way analysis of variance/Tukey’s multiple comparison test; #difference in HTV ATB vs. HTV Ctrl; *as indicated, */#P < 0.05, **/##P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001
