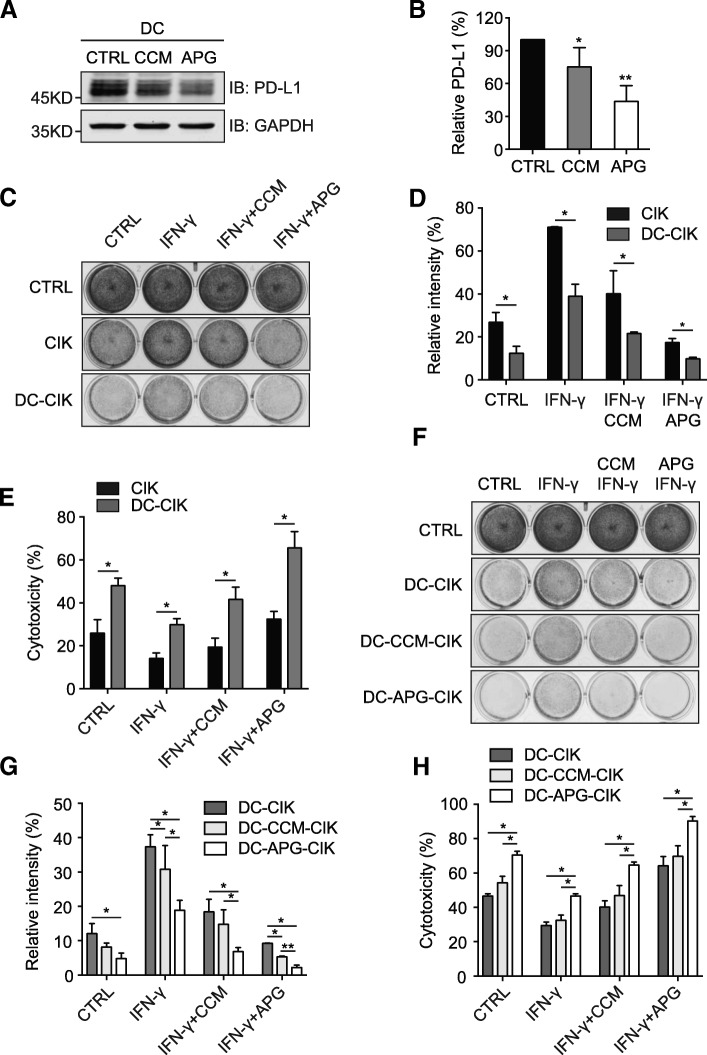
Fig. 7.
Apigenin decreases PD-L1 expression in DCs to augment host T cell immunity. a human PBMC-derived DCs were treated with curcumin or apigenin for 24 h and PD-L1 expression was examined by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. b quantitation of relative PD-L1 levels from A (control as 100%). c A375 killing assays with CIK and DC-CIK cells. Experimental procedures were described in the methods. d quantitation of the intensity of surviving A375 cells from C (control set as 100%). e cytotoxicity of CIK and DC-CIK cells against A375 as described in C was analyzed using an LDH assay kit. f control, curcumin and apigenin-treated DCs were used in cocultures with CIK cells to generate DC-CIK, DC-CCM-CIK, and DC-APG-CIK, respectively, which were then used in A375 killing assays at an effector to target ratio of 10:1 for 20 h. Surviving A375 cells were stained with crystal violet and imaged. g quantitation data of relative intensities from surviving A375 cells in F (control set as 100%). h cytotoxicity of various DC-CIK cells against A375 was analyzed using an LDH assay kit. Error bars represent S.D. (n = 3, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01)