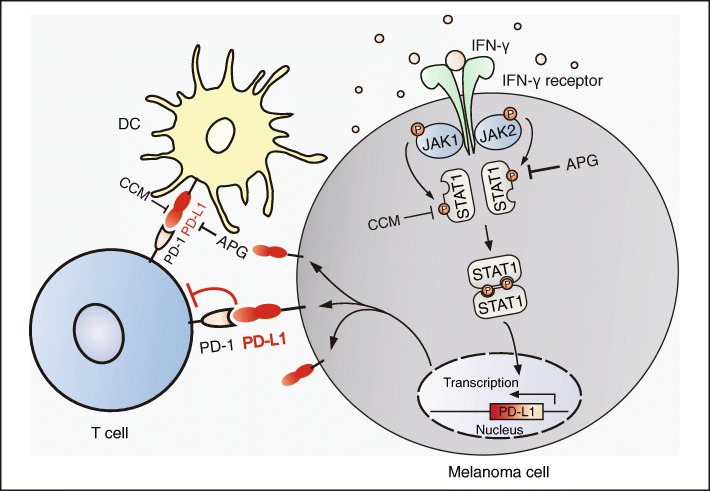
Fig. 8.
Schematic diagram depicting apigenin and curcumin-mediated inhibition of PD-L1 expression in DCs and melanoma cells. Apigenin and curcumin inhibit IFN-γ-induced STAT1 phosphorylation, leading to reduced PD-L1 expression and surface presentation. Apigenin shows stronger effects than curcumin, with the suppression of PD-L1 expression exerting a dual effect via regulating both tumor and antigen presenting cells (DCs)