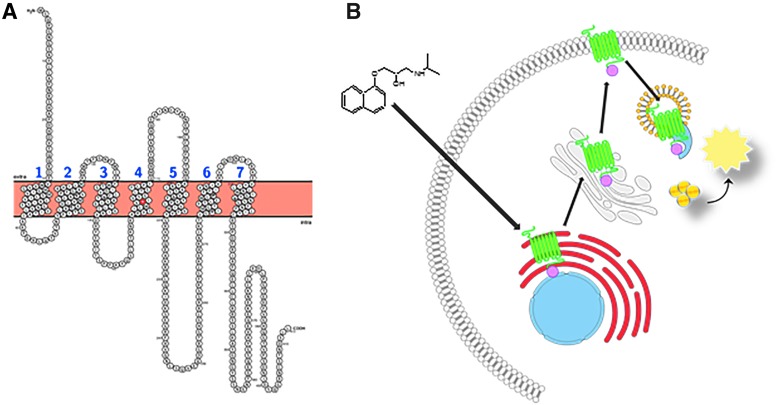
Fig. 1.
Snake plot of ADRB2. Full-length snake plot showing the amino acid sequence of the human ADRB2 receptor. The tryptophan residue residing in the fourth transmembrane domain (W158) that is mutated to facilitate ER retention is highlighted in red. Membrane spanning domains are numbered sequentially (N-term to C-term) in blue (A). Diagram of the cell-based ADRB2 pharmacochaperone assay. Mutated ADRB2 harboring the single amino acid substitution (W158A) and the pro-link tag is retained in the ER by the cell's quality control systems. Upon binding to the target, a cell-permeable ligand (such as propranolol, given here) induces forward trafficking through the ER (red) and Golgi (gray), and ultimately to the plasma membrane. There it is internalized through the endosome (yellow) where the PK-tagged receptor can physically interact with the EA reconstituting a functional β-gal enzyme. The addition of lysis buffer and substrate produces light (B). ADRB2, beta-2-adrenergic receptor; β-gal, beta-galactosidase; EA, enzyme acceptor; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; PK, ProLink.