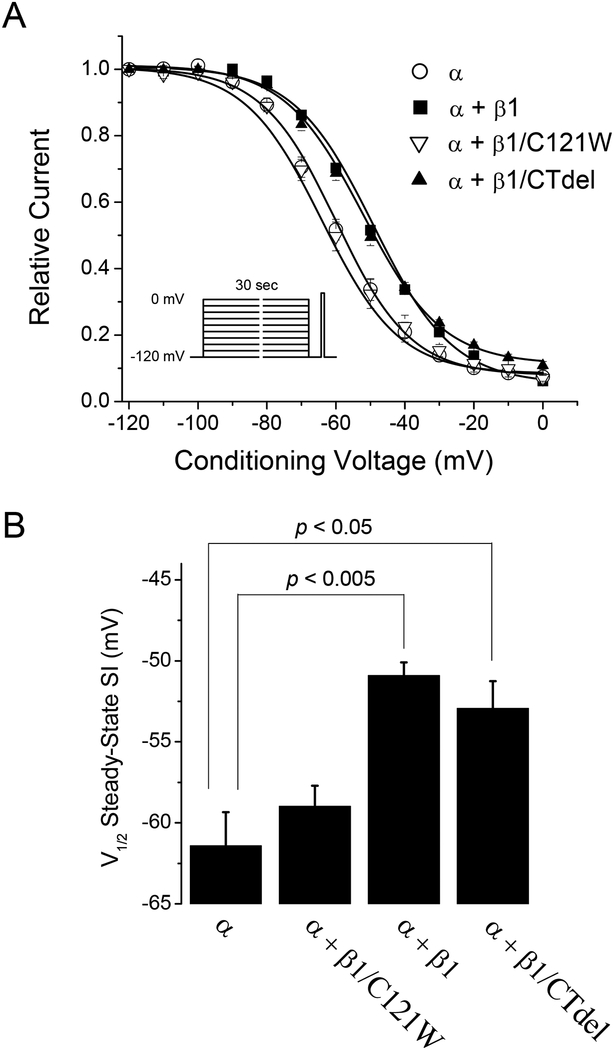
FIGURE 3.
The β1 subunit mildly impedes steady-state slow inactivation. The voltage dependence of slow inactivation was measured as the peak current elicited by a test depolarization to −10 mV after 30-s conditioning pulses ranging from −120 to 0 mV (inset). Conditioning and test pulses were separated by a 20-ms recovery gap at −120 mV to remove fast inactivation. (A) Coexpression of the wild-type β1 subunit (α + β1, ■) or the β1 C-terminal deletion (α + β1/CTdel, ▲) depolarized (right-shifted) the voltage-dependence of steady-state slow inactivation compared to expression of α-subunit alone (α, ○) or coexpressed with the β1 N-terminal mutation C121W (α + β1/C121W, ∇). (B) Voltage of half-inactivation (V1/2) for steady-state slow inactivation was depolarized by ~10mV upon coexpression of wild-type β1 (p < 0.005), and β1/CTdel (p < 0.05) compared to α-subunit alone, while V1/2 for β1/C121W was not significantly different.