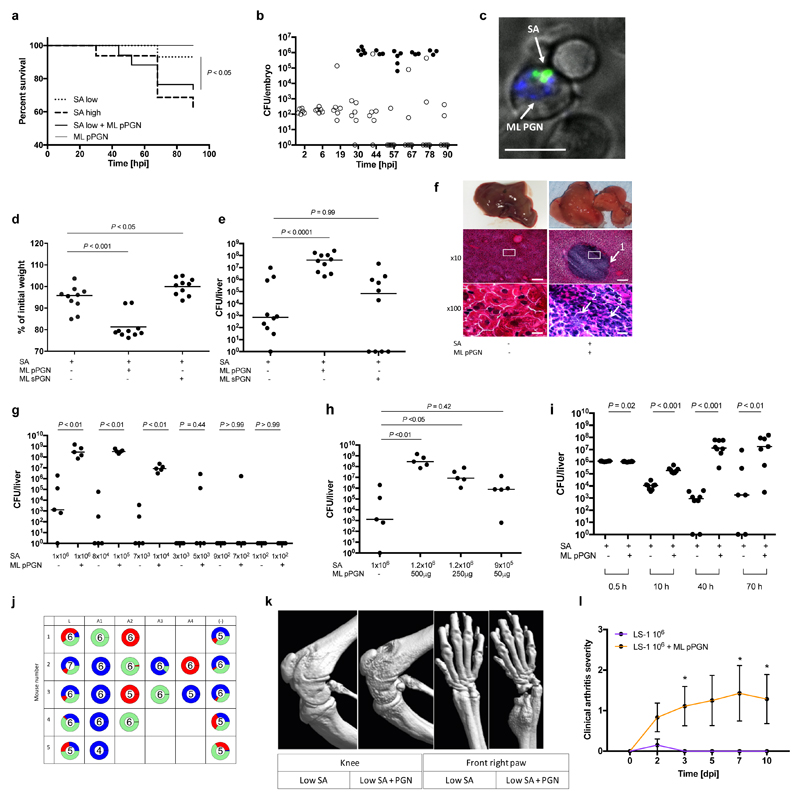
Figure 2. Gram-positive PGN augments S. aureus pathogenesis in animal models.
a, Survival curves of fish injected with low dose S. aureus SH1000 (150 CFU, SA low) and 5 ng polymeric M. luteus PGN (ML pPGN). S. aureus SH1000 high dose (1500 CFU, SA high) was injected as a positive control. Data are representative of three independent experiments; n ≥ 28, log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. b, Growth of bacteria within embryos after co-injection with low dose S. aureus SH1000 (150 CFU) and 5 ng M. luteus PGN. Open circles, live and filled circles, dead embryos. n ≥ 60. c, In vivo imaging of Alexafluor 647 (blue) labelled M. luteus PGN (5 ng, ML PGN indicated by arrow) and S. aureus SH1000-GFP (150 CFU, SA indicated by arrow) 2 hpi. Within the zebrafish circulation valley, phagocytes were viewed at x 60 magnification). Images are representative of 5 embryos from two independent experiments. Scale bar 10 μm. d, e, BALB/c mice were injected i.v. with low dose (1x106 CFU) S. aureus NEWHGkan with or without 500 μg M. luteus particulate PGN (pPGN) or soluble PGN (sPGN). Weight loss (d) and liver (e) CFU were measured. n = 10 per group; median value shown, Mann-Whitney two-sided test. f, Representative images of histopathological changes during infection. Arrows show 1, large abscess within liver parenchyma; 2, accumulation of extracellular S. aureus; 3, dense infiltrate of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). Inset box at x10 magnification (scale bar 100 μm) is displayed at x100 (scale bar 10 μm) in bottom panels. n = 5 per group. g, Liver CFU recovered from BALB/c mice injected i.v. with a decreasing dose of S. aureus NEWHGkan with or without 500 μg M. luteus pPGN. n = 5 per group; median value shown, Mann-Whitney two-sided test. h, Liver CFU recovered from BALB/c mice injected i.v. with low dose (1x106 CFU) S. aureus NEWHGkan with or without a decreasing dose of M. luteus pPGN. n = 5 per group; median value shown, Mann-Whitney two-sided test. i, Liver CFU at various time points after co-injection of low dose (1x106 CFU) S. aureus with or without 500 μg M. luteus pPGN. n = 8 per group; median value shown, Mann-Whitney two-sided test. j, Livers from mice injected with low dose (1x106 CFU; 1:1:1 mixture of NewHG EryR, TetR or KanR, n = 5 per group S. aureus NEWHGkan plus 500 μg M. luteus PGN were harvested. Individual abscesses were dissected and bacterial CFU enumeration from each abscess was determined (A1-A4). Bacterial CFUs from residual liver tissue post dissection (-) was also enumerated and added to the abscess CFUs to provide a total CFU count for each liver (L). k, Micro-CT imaging of knee and front right paw of an NMRI mouse injected i.v. with low dose (1x106 CFU) S. aureus LS-1 with or without 1 mg M. luteus pPGN. Images are representative of 10 animals. l, Clinical arthritis severity of NMRI mice injected i.v. with S. aureus LS-1 low dose (1x106 CFU) and 1 mg M. luteus pPGN. dpi, days post infection. n = 10 per group; error bars, mean and s.e.m, Mann-Whitney two-sided test. * P < 0.05.