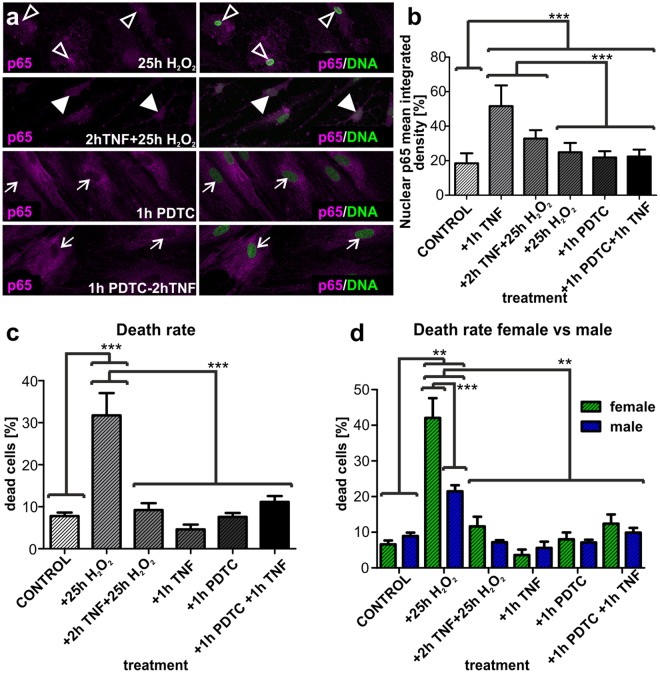
Figure 5.
Treatment of ITSC-derived glutamatergic neurons with TNF-α prevents from oxidative stress-mediated cell death in a sex-dependent manner. (a) Immunocytochemistry of ITSC-derived neurons after 30 days of differentiation, after treatment with H2O2 alone, TNF-α-pre-treatment prior to H2O2, PDTC alone and PDTC followed by TNF-α against NF-κB-p65. (b) Quantification of immunocytochemical assays showed significantly increased nuclear translocation of NF-κB-p65 after treatment with TNF-α alone and TNF-α prior to H2O2 compared to H2O2 alone and untreated control. Pre-treatment of ITSC-derived neurons with PDTC for one hour followed by TNF-α-treatment did not result in significantly different amounts of nuclear NF-κB-p65 compared to PDTC alone. Mean values were normalized to the highest value. (c) Quantification of neuronal cell death showed significant death after oxidative stress insult (H2O2) compared to TNF-α/ H2O2, TNF-α, PDTC, PDTC/TNF-α and untreated control (n = 6). (d) Quantification of neuronal cell death after oxidative stress (H2O2), TNF-α-pre-treatment, TNF-α, PDTC, PDTC/ TNF-α and untreated control comparing sex differences (n = 3 males, n = 3 females). Data were showed not to be normally distributed using Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk normality tests. Non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test was further used (p ≤ 0.001), and Tukey’s post-hoc test (**p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001). Mean ± SEM (standard error of the mean).