Fig. 3.
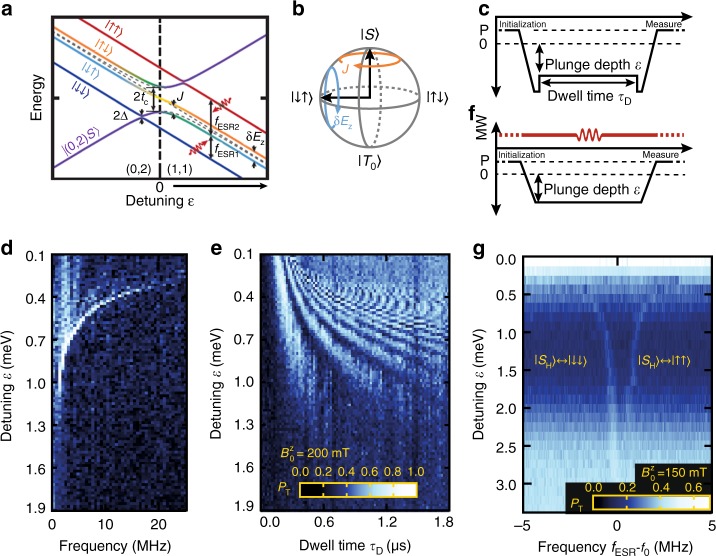
Exchange drive oscillations and individual electron ESR at low field. a Energy diagram for the five lowest energy states near the (0, 2)–(1, 1) anti-crossing represented in the spin basis. Compared to Fig. 2a, an increased magnetic field splits off polarized triplets while δg due to the SO coupling breaks the degeneracy producing δEZ. b Bloch sphere representation of the qubit showing effect of the Heisenberg exchange J and δEZ c, d Coherent Rabi oscillations between and states, driven by exchange J. c Pulse sequence for data in d and e; adiabatic ramp (diabatic through the SH/T− crossing) prepares (assuming g2 > g1). Diabatic pulses back to the high exchange region then causes coherent evolution of the state for a period of variable time/depth. The resulting change in population of is mapped back to using the inverse adiabatic ramp. d Fourier transform of time series e which shows exchange driven oscillations between the and states. f Pulse sequence used for data in g. g Triplet probability as a function of detuning ε and applied ESR frequency with f0 = 4.205 GHz. ESR spin rotations of the spin in the left dot (upper branch) and right dot (lower branch), using an on-chip microwave ESR line. is prepared similar to b, a 25 μs ESR pulse of varying frequency is applied rotating when = fESR, and , when = fESR; is again mapped back . We find = (0.43 ± 0.02) × 10−3