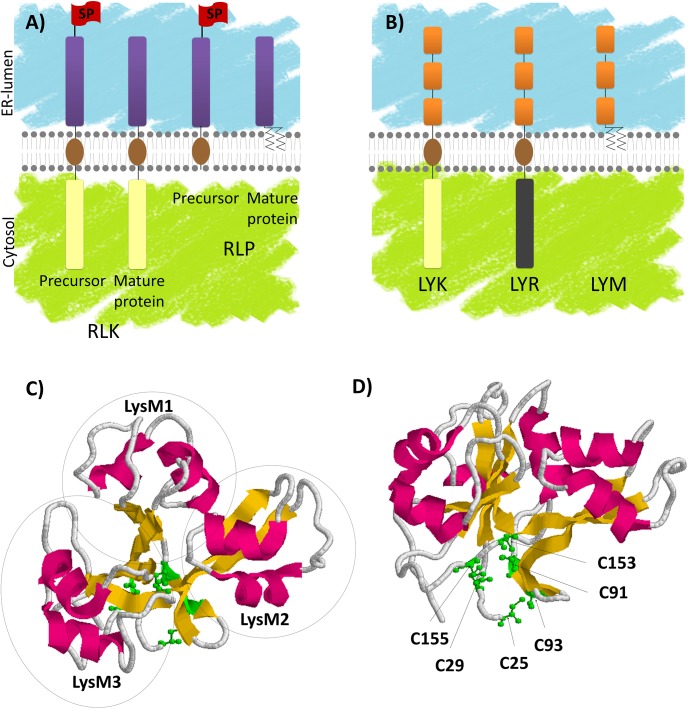
FIGURE 1.
LysM-RLK and LysM-RLP structure, synthesis and maturation. (A) Receptor-like kinases (RLKs) are produced by ribosomes associated with the ER. The ECR that is preceded by a SP is translocated into the ER lumen during translation until the TM (brown) is inserted in the lipid bilayer. The ICR is then produced in the cytosol. SPs are cleaved in the ER and the mature proteins are transported through the secretory pathway to their final destinations, mainly the plasma membrane. GPI anchored receptor-like proteins (RLPs) are also produced by ribosomes associated with the ER. After translocation and insertion in the membrane, the SP is cleaved and the ECR is transferred to a GPI anchor. The mature proteins are then transported to their final destinations. (B) LysM-RLKs are composed of 3 lysin motifs (LysM, orange) in the ECR, a TM (brown) and an ICR bearing an active kinase (beige, LYK subfamily) or an inactive kinase (gray, LYR subfamily). LysM-RLPs (LYMs) are composed of 3 LysMs in the ECR attached to a GPI anchor. (C,D) AtCERK1 3D structure resolved by Liu T. et al. (2012). Images were obtained using the pdb file 4EBY: α-helices are indicated in pink, β-strands are indicated in yellow and C residues are indicated in green. (C) Orientation of AtCERK1 ECR highlighting the 3 LysMs (circled) packed together. (D) Orientation of AtCERK1 ECR highlighting the C residues involved in disulfide bridges.