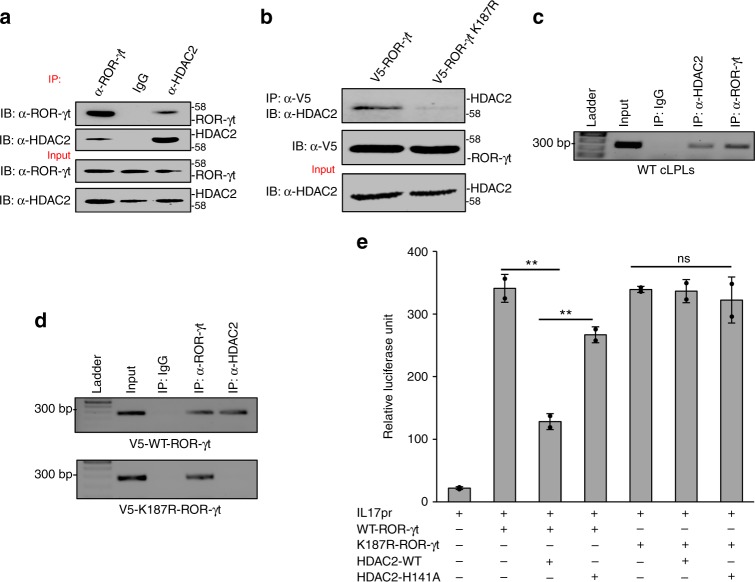
Fig. 4.
SUMOylation facilitates HDAC2-to-ROR-γt binding and inhibits IL-17 expression. a Lysates from cLPLs of WT mice were immunoprecipitated with anti-ROR-γt, anti-HDAC2 antibody, or control IgG antibody and immunoblotted with antibody against ROR-γt or HDAC2. b Transduced ROR-γt–/– CD4+ T cells expressing either WT-ROR-γt or the K187R-ROR-γt were immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 antibody and immunoblot with antibody against V5 or HDAC2. c Binding of HDAC2 to the IL-17 promoter was assessed by ChIP analysis using a DNA-protein complex from cLPLs of WT mice that was immunoprecipitated with anti-ROR-γt, anti-HDAC2, or control IgG antibody. d SUMOylation of ROR-γt facilitates HDAC2 recruitment to the IL-17 promoter. ChIP analysis was conducted using DNA-protein complex from transduced ROR-γt–/– CD4+ T cells expressing either WT-ROR-γt or the K187R-ROR-γt and immunoprecipitated with anti–ROR-γt, anti-HDAC2, or control IgG antibody. e A luciferase assay was performed of lysates from Jurkat T cells transfected with various combinations (below plot) of IL-17-promoter-driven luciferase plasmid (pGL4-mIL17p), plasmid encoding WT-ROR-γt or K187R-ROR-γt along with either HDAC2-WT or HDAC2-H141A. Results are presented in relative luciferase units (RLU). Data are from one experiment representative of three or more independent experiments with similar results. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01, ns: non-significant (two-tail t test) error bars are S.D.