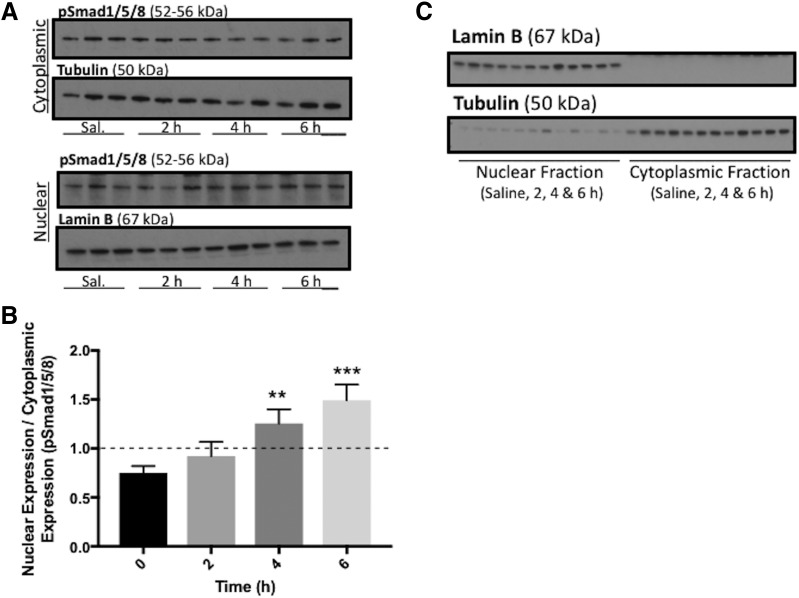
Fig. 5.
BMP-9 treatment increases expression of nuclear pSmad1/5/8 in rat brain microvessels. (A) Animals were administered a single dose of BMP-9 (1 μg/kg, i.p.) or 0.9% saline and treated for 2–6 hours. Animals were sacrificed and brain microvessels were isolated and subjected to nuclear and cytoplasmic fractionation, which was then prepared for western blot analysis. Fractionated samples (10 μg) were resolved on a 4%–12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membrane and analyzed for expression of pSmad1/5/8. (B) Relative levels of pSmad1/5/8 expression were determined by densitometric analysis and normalized to α-tubulin for cytoplasmic fraction and lamin B for nuclear fraction as loading controls. Nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio was then determined. (C) Quality of fractionated samples derived from rat brain microvessels was assessed. Western blot analysis was performed where the cytoplasmic fraction was analyzed for expression of lamin B, a nuclear marker protein. Similarly, the nuclear fraction was examined for expression of tubulin, a cytoplasmic marker protein. Drug-treated groups were compared with control groups, i.e., 0.9% saline-injected animals. Western blot data are reported as mean ± S.D. from at least three independent experiments, where each treatment group consisted of three individual animals (n = 3). Asterisks represent data points that were significantly different from control (saline-treated) animals (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).