Fig. 1.
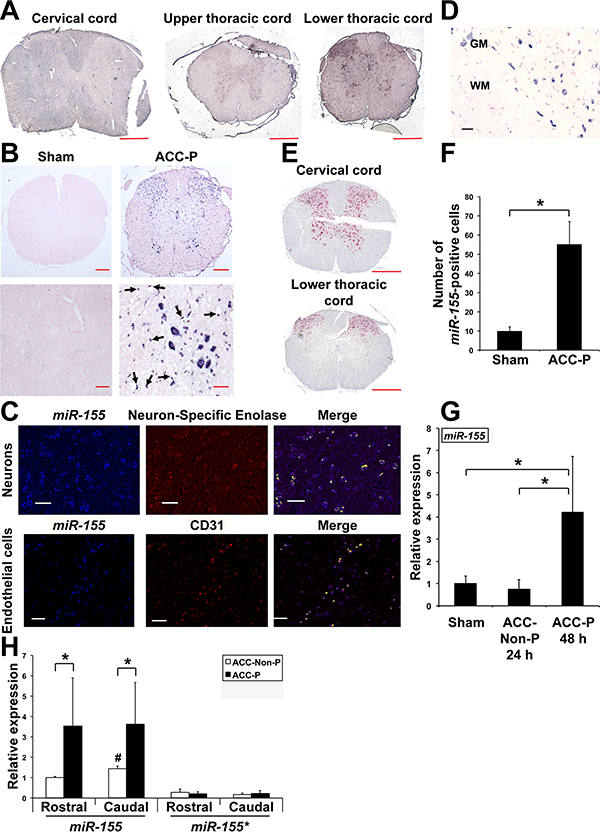
Up-regulation of miR-155 expression in SC of ACC-P WT mice. (A) In situ hybridization showing miR-155 expression on three cross sections of spinal cord of the same mouse 48 h following ACC. Scale bars = 400 μm. (B) Representative in situ hybridization for miR-155 on cross sections of the lower thoracic part of SC (44–48 h following ACC) of four sham and four ACC-P mice. Right lower panel: black arrows point to miR-155-positive endothelial cells of blood vessels. Counterstain is nuclear fast red. Top panels: scale bars = 200 μm. Lower panels: scale bars = 40 μm. (C) MiR-155 expression in neurons of WT mice was assessed using an antibody to Neuron-Specific Enolase neuronal marker. MiR-155 expression in endothelial cells was assessed using an antibody to CD31. Yellow: co-expression. Scale bars = 125 μm. (D) MiR-155 expression in wild type ACC-Paralyzed mice is primarily detected in spinal cord gray matter. WM, White matter. GM, Gray matter. Scale bar = 100 μm. (E) NeuN expression in ventral horns of lower thoracic spinal cord following ACC; note loss of expression corresponds to high miR-155 expression. Scale bars = 400 μm. (F) Number (Mean + SD) of miR-155 positive cells on cross-sections of the thoracic and lumbar regions of SC of sham (n = 4) and ACC-P (n = 4) mice 44–48 h after ACC (3 counts/ mouse). *, P < 0.0042. (G) MiR-155 expression (Mean + SD) in the caudal region of the spinal cord of sham (n = 5), 24 h ACC-Non-P (n = 5) and 44–48 h ACC-P (n = 4) WT mice was determined by qRTPCR. *, P < 0.0459. Values were normalized to sham. (H) MiR-155 and miR-155* expression (Mean + SD) in the rostral and caudal regions of SC of ACC-Non-P (n = 4) and ACC-P (n = 7) WT mice was determined by qRT-PCR 44–48 h after ACC. *,P < 0.031;#, caudal ACC-Non-P different from rostral ACC-Non-P, P < 0.0016. Values were normalized to rostral ACC-Non-P miR-155. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
