Figure 1:
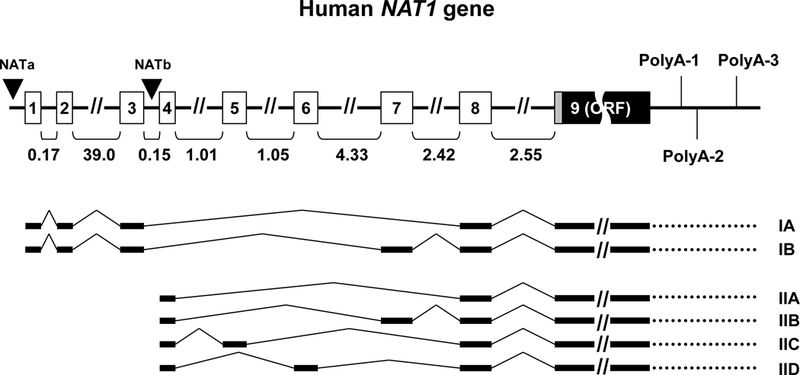
Overview of NAT1 gene structure and main alternative transcripts. The gene comprises 8 non-coding exons differentially spliced to generate alternative transcripts with variable 5’-UTRs. Exon 9 contains the entire open reading frame (ORF) of the gene, as well as the adjacent 3’-UTR terminated after three differentially utilized polyadenylation signals located at 213 (polyA-1), 331 (polyA-2; major) and 734 (polyA-3) nucleotides downstream of the coding exon. Type I transcripts (A,B) are initiated by promoter NATa located upstream of non-coding exon 1. Type II transcripts (A-D) are initiated by promoter NATb (major) located upstream of non-coding exon 4. The size of introns (in kilobases) is indicated below the gene. The figure was compiled from information previously published [7–9, 12] (figure not drawn to scale).
