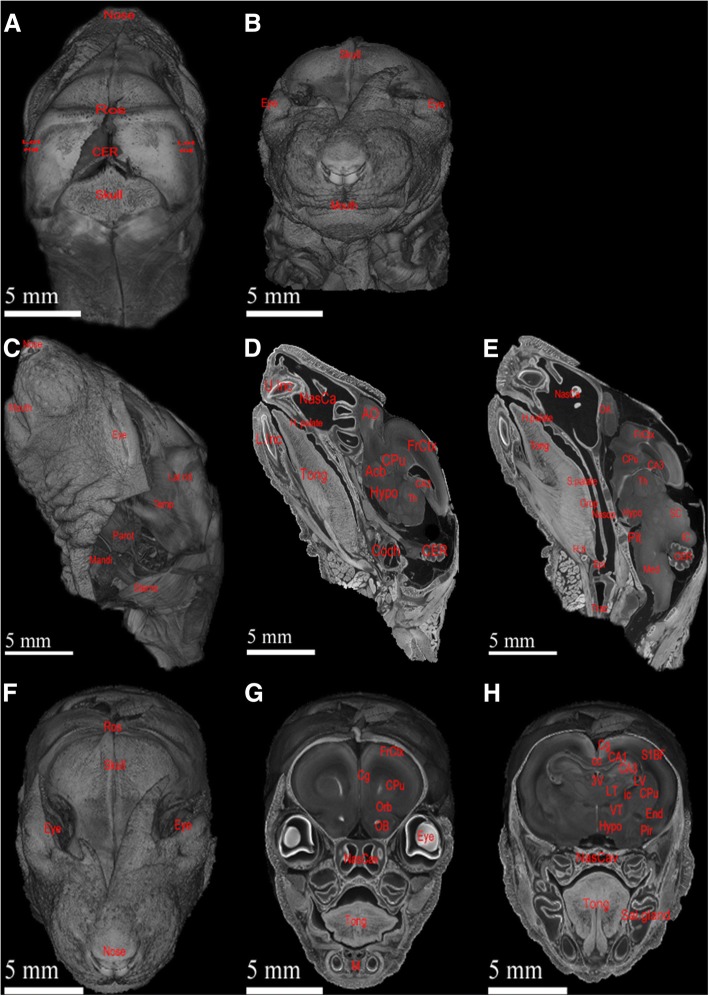
Fig. 3.
Volumetric rendering of ex vivo micro-CT scan of neonatal rat’s head enables detailed visualization and potential high-powered quantitative analysis. (a and b) illustrate respective anterior and posterior views of external features of rat’s head and neck, including mouth, nose, and muscle distributions. (c, d, and e) are respective external, parasagittal, and sagittal views of rat’s head and neck. (f, g, and h) are progressive coronal explorations of the same rat. These different views demonstrate the high-resolution power and flexibility of micro-CT scans. These exploration images show blood vessels, parotid glands, nasal anatomy, oral anatomy, and intracranial anatomy along with obvious muscular features throughout the head. Anatomical structures are labelled as follow: Acb = accumbens nucleus; AO = anterior olfactory bulb; apons = anterior pons; ATh = anterior thalamus; CA1 = CA1 field of hippocampus; CA3 = CA3 field of hippocampus; cc = corpus callosum; CER = cerebellum; Cg = cingulate gyrus; Coch = cochlea; CPu = caudate putamen; End = Endopiriform nucleus; Epi = epiglottis; EPi = external plexiform layer; FrCtx = frontal cortex; H. b = hyoid bone; H. palate = hard palate; Hypo = hypothalamus; IC = inferior colliculus; ic = internal capsule; Lat rid = lateral ridge of skull; L. Inc = lower incisor; LT = lateral thalamus; LV = lateral ventricle; M = mandible; Mandi = mandibular gland; Med = medulla; NasCa = nasal cavity; Nasop = nasopharynx; OB = olfactory bulb; Orb = orbital cortex; OV = olfactory ventricle; Parot = parotid gland; Pir = piriform cortex; Pit = pituitary gland; PTh = posterior thalamus; ROS = rostral ridge of skull; Sal. Gland = salivary gland; SC = superior colliculus; S. palate = soft palate; S1BF = Somatosensory 1 Barrel Field; Sterno = sternomastoideus; Temp = temporalis; 3 V = 3rd ventricle; Th = thalamus; Tong = tongue; Trac = trachea; U. Inc = upper incisor; VT = ventral thalamus