Figure 2.
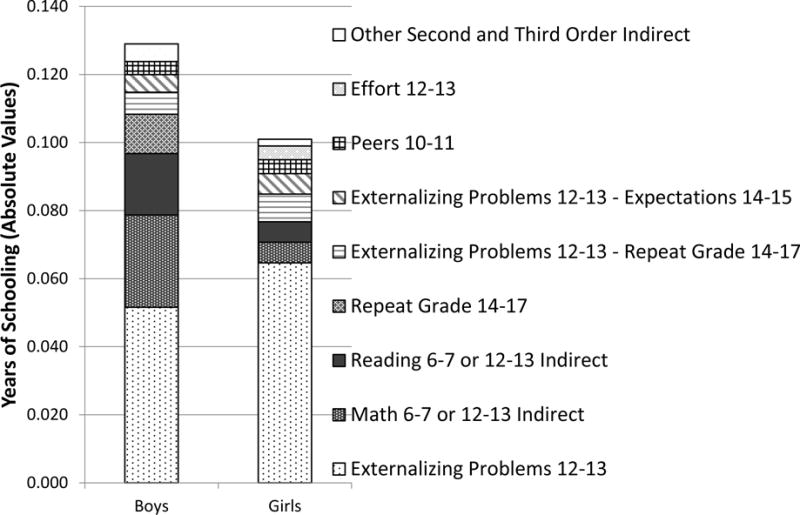
Mediators of the Indirect Path between Early Externalizing Problems and Years of Schooling (i.e., Mediators of the Indirect Effect of Early Externalizing Problems on Schooling), by Gender (NFemales = 881, NMales = 780)
Note: Only pathways greater than .001 SD in magnitude are displayed; other pathways are subsumed within “other indirect paths.” The term “indirect effect” in the title reflects statistical usage of the term: the components of each stacked bar chart encompass all mediating paths (those not captured through the single coefficient linking early externalizing problems and educational attainment).
Source: The 1983 to 1986 birth cohorts of the Children of the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth:1979 (NLSY-C) and matched National Longitudinal Survey of Youth:1979 (mother sample). The low-income white and military oversamples are excluded. The National Longitudinal Survey of Youth-Child Supplement (NLSY-C) consists of a nationally representative sample of children born to women age 14 to 21 in 1979; after excluding the poor white and military oversamples, the working sample in this study is restricted to the 1,857 children born 1983 to 1986, whose mothers were therefore 18 to 29 years at birth. Children born 1983 to 1986 were born early enough to be age 26 to 29 as of the 2012 followup survey, but late enough to have early behavior problems information measured at age 4 to 5 beginning in 1986, at which point these items were introduced for children age 4 to 16. I used multiple imputation of 20 datasets to handle item-missingness. Model estimates use inverse-probability weighting to deal with stratified sample design (minority oversampling) and sample attrition by the 2012 follow-up wave (weights are described at: https://www.nlsinfo.org/weights/nlsy79). Once inverse-probability survey weights are applied, the working sample with complete attainment and behavior information drops from 1,857 to 1,661 children (881 girls, 780 boys).
