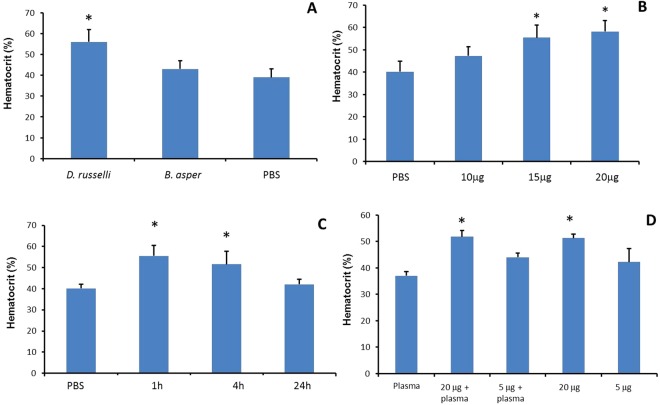
Figure 1.
Hemoconcentration induced by D. russelii venom. (A) Mice received an i.m. injection, in the right gastrocnemius, of 20 µg of D. russelii or B. asper venom, dissolved in 100 µL PBS, and hematocrit was determined 1 h after injection. Controls received PBS alone. Only D. russelii venom induced hemoconcentration. (B) When mice received various doses of D. russelii venom, under otherwise identical conditions, hemoconcentration developed with the dose of 15 µg and higher. (C) Time course of hemoconcentration after i.m. injection of 20 µg of D. russelii venom in mice. (D) Effect of plasma on the hemoconcentration effect. When injected i.m., plasma itself did not induce the effect. The increases in hematocrit induced by 20 µg D. russelii venom diluted either in PBS or plasma were essentially equivalent. Results are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 5). In A, B and C, *p < 0.05 when compared to hematocrit of mice receiving PBS alone. In D, *p < 0.05 when compared to the other treatments.