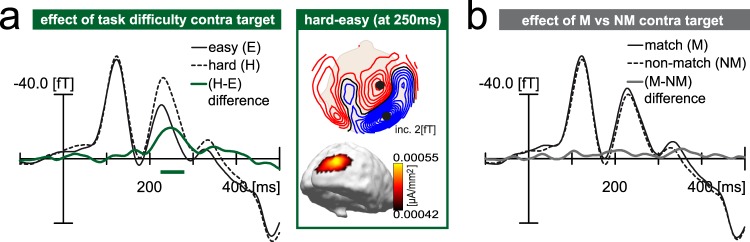
Figure 4.
ERMF response to the target (Experiment 1). (a) Effect of discrimination difficulty on target-related effects. The waveforms show the brain response contralateral to the target on easy (E, black solid) and hard (H, black dashed) trials as well as the hard-minus-easy difference (green solid). The maps on the right show the field distribution and current source density estimate for the hard-minus-easy difference at the respective modulation maximum. The posterior parietal brain response to the discrimination target is significantly enhanced for the high discrimination difficulty targets (hard task) between 225ms-280ms as indicated by the green bar (p < 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons, as described in Methods). (b) The waveforms show the brain response contralateral to the target (same sensors as in (a)) for match (M, black solid) and non-match (NM, black dashed) trials as well as the match-minus-non-match difference (grey solid). Sliding window t-tests reveal no significant modulation of the target response by a colour match between the target and probe.