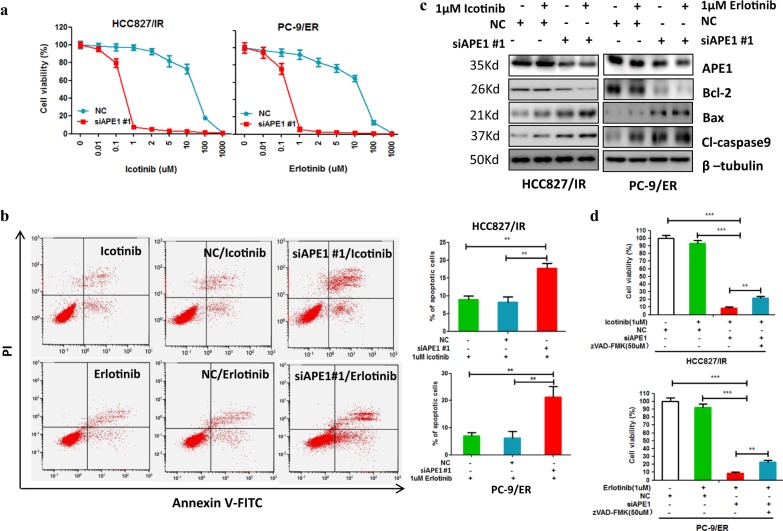
Fig. 3. Silencing of APE1 enhanced the sensitivity of TKI-resistant LUAD cells to TKIs treatment.
a Silencing of APE1 significantly enhanced TKI-induced cell growth inhibition in TKI-resistant LUAD cells. Indicated cells were transfected with APE1 siRNA or negative control nucleotides (NC). After 24 h of transfection, cells were treated with indicated TKIs for 72 h, and cells were then subjected to cell viability assay. b Silencing of APE1 significantly increased TKIs-induced apoptosis in TKI-resistant LUAD cells. HCC827/IR and PC-9/ER cells were transfected with or without APE1 siRNA. After 24 h of transfection, cells were treated with indicated TKIs for 48 h, and cells were then subjected to flow cytometry assay. c Combination treatment of APE1 silencing and TKI significantly increased pro-apoptotic protein expression while suppressing the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins in TKI-resistant LUAD cells. Indicated cells were transfected with siRNA of APE1 or negative control oligonucleotides (NC), then treated with indicated TKIs. After 48 h of TKI treatment, cells were subjected to Western blotting. d Caspase inhibitor zVAD-FMK treatment inhibited silencing of APE1 enhanced cell viability inhibition effects of TKIs in TKI-resistant LUDA cells. Indicated cells were transfected with siRNA of APE1 (siAPE1) or negative control oligonucleotides (NC). After 24 h of transfection, cells were reseed in 96-well plates. After overenight, cells were treated with indicated drugs for 48 h, then subjected to cell viability assay. **p < 0.01