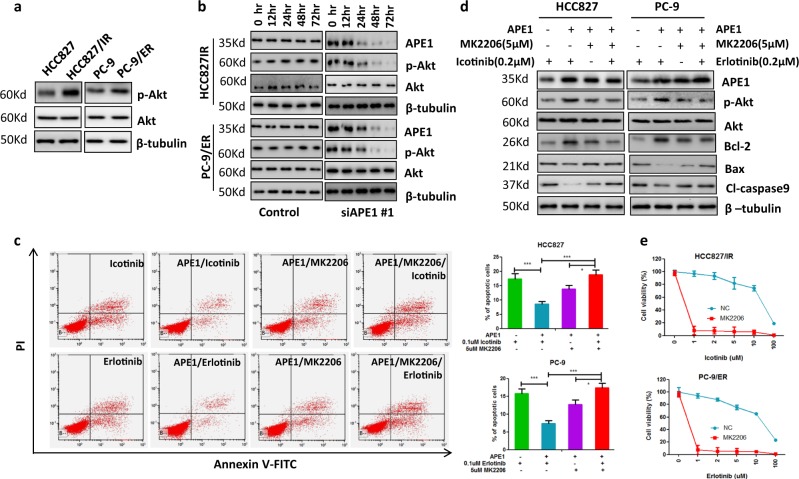
Fig. 5. APE1 contributes to TKI resistance through activating Akt.
a p-Akt was increased in TKI-resistant LUAD cells compared to their parental cells. b Silencing of APE1 significantly inhibited Akt phosphorylation in TKI-resistant LUAD cells. Indicated cells were transfected with APE1 siRNA, then subjected to Western blot analysis at indicated times. c Inactivation of Akt inhibited APE1 overexpression-caused inhibition of TKI-induced apoptosis in LUAD cells. Indicated cells were transfected with or without the APE1 expression plasmid. After 24 h of transfection, cells were treated with indicated drugs for 48 h, then subjected to apoptosis analysis. d Inactivation of Akt suppressed APE1 overexpression-induced stimulation of anti-apoptotic proteins’ expression and inhibition of pro-apoptotic proteins’ expression. Indicated cells were transfected with or without the APE1-expressing plasmid. After 24 h of transfection, cells were treated with indicated drugs for 24 h. Then, cells were subjected to Western blotting. e Treatment with Akt inhibitor significantly enhanced TKI-induced cell growth inhibition in TKI-resistant LUAD cells. Indicated cells were treated with indicated TKI and 5 µM of MK2206 for 72 h, then subjected to cell viability assay. *p < 0.05’; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001