Fig. 2.
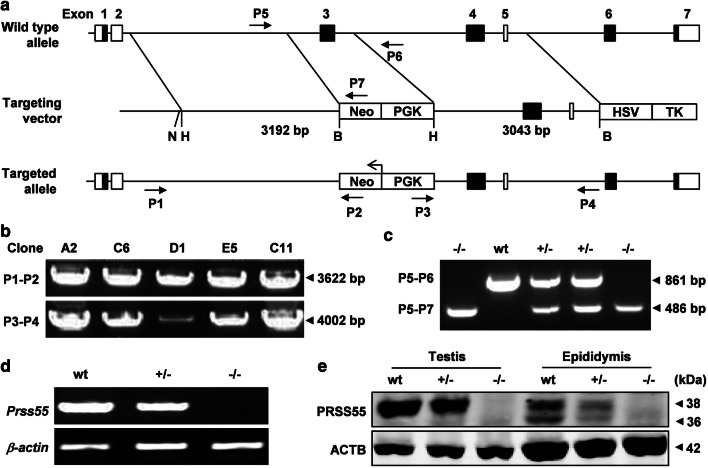
Generation of Prss55-KO mice. a The targeting strategy for disruption of the mouse Prss55 gene. The boxes in black represent the exons with coding region. The targeting vector contains 3192 bp of 5′ and 3043 bp of 3′ homologous fragments. PGK-Neo and HSV-TK were used for positive and negative selections, respectively. P1-P7, the primers for genotyping and their relative positions, are indicated. N, NotI; H, HindIII; B, BamHI. b PCR on genomic DNA from ES cell clones was performed using the primers P1 and P2 for the 5′ arm and P3 and P4 for the 3′ arm. c Triple primer PCR on mouse tail genomic DNA was performed using primers P5-P7 as routine genotyping of mice. The expected size of PCR products (arrowheads) is shown on the right of the images. d RT-PCR for the expression of Prss55 mRNA in the testis of adult mice with three different genotypes. Actb was used as an internal control. e Western blot analysis of PRSS55 protein in the testis and epididymis of adult mice with three different genotypes. ACTB was used as a loading control