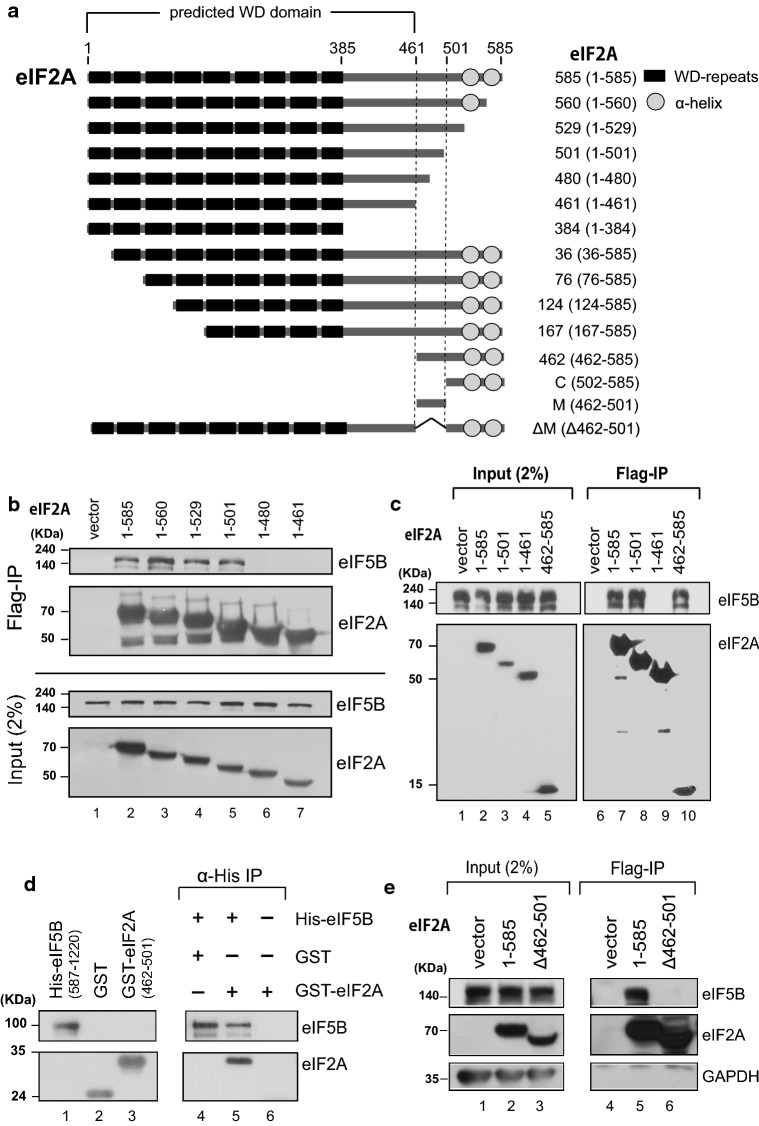
Fig. 2.
Determining the eIF2A domain required for the interaction with eIF5B. a Schematic diagram of eIF2A and its derivatives. b, c Immunoprecipitation was performed using lysates of 293FT cells expressing Flag-tagged eIF2A derivatives. Flag-tagged eIF2A proteins were precipitated with Flag resin, and the endogenous eIF5B proteins associated with the eIF2A derivatives were visualized by western blotting with anti-eIF5B (ProteinTech Group), anti-Flag (Sigma), and anti-GAPDH (AbD Serotec). d Co-precipitation of purified eIF2A and eIF5B. His-tagged eIF5B (587–1220) and GST-fused eIF2A (462–501) polypeptides were mixed, and the former was precipitated with an anti-His-conjugated resin. Co-precipitated GST–eIF2A (462–501), which corresponds to the M domain, was visualized by western blotting with anti-GST. e Co-precipitation experiments were performed as described in panels (b, c), except that we used a plasmid encoding Flag-eIF2A (Δ462–501)