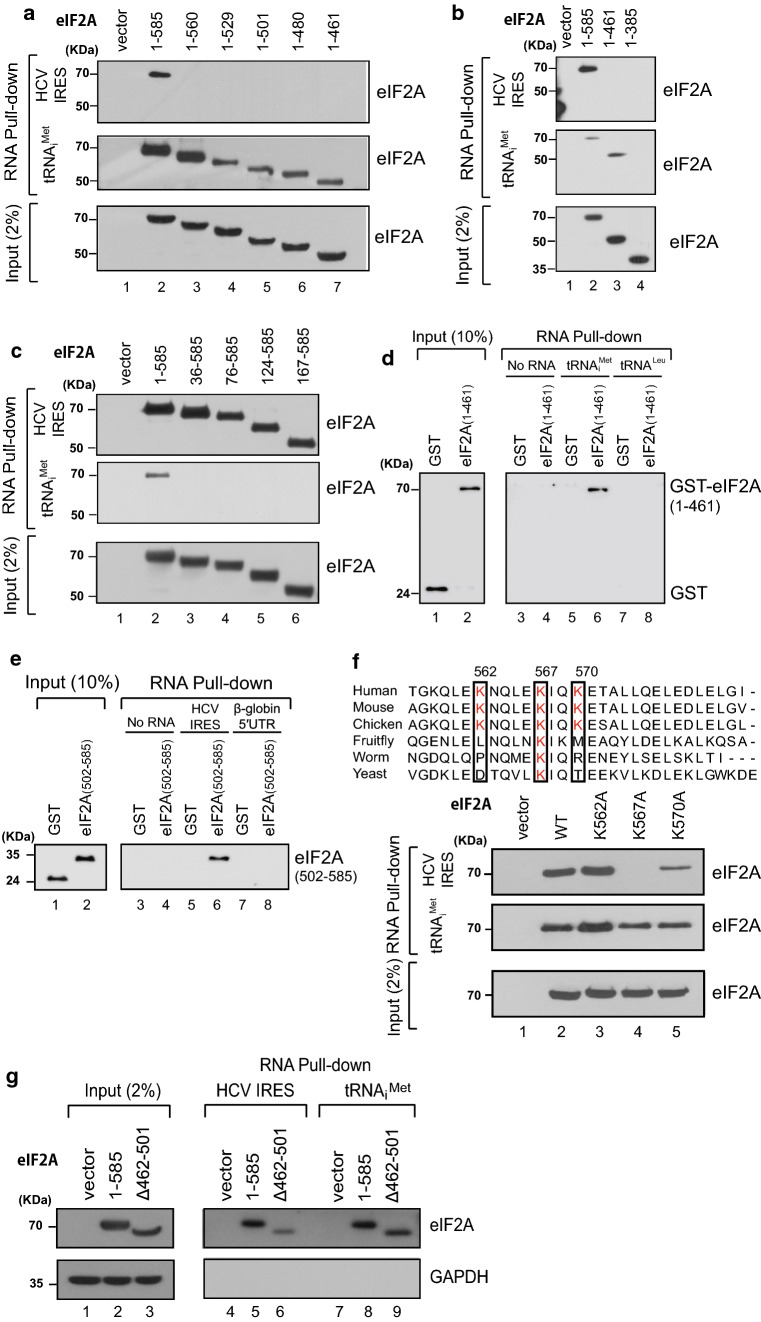
Fig. 3.
Determining the eIF2A domain required for binding to tRNAMeti and the HCV mRNA. a–c RNA pull-down experiments were performed with biotinylated tRNAMeti and a biotinylated HCV RNA corresponding to the IRES element (HCV IRES), using lysates of 293FT cells transfected with plasmids expressing various Flag-tagged deletion mutants of eIF2A. The RNA-bound proteins were precipitated with streptavidin-conjugated agarose resin and visualized by western blotting with anti-Flag (Sigma). d RNA pull-down experiments were performed with biotinylated RNAs (tRNAMeti and tRNALeu) and purified recombinant protein GST-fused eIF2A (1–461), which corresponds to the WD domain. e RNA pull-down experiments were performed with biotinylated RNAs (HCV IRES and β-globin 5′UTR) and purified GST–eIF2A (502–585), which corresponds to the C domain. f RNA pull-down experiments were performed with biotinylated tRNAMeti and biotinylated HCV IRES using lysates of 293FT cells expressing various substitution mutants of Flag-tagged eIF2A. g RNA pull-down experiments were performed with biotinylated tRNAMeti and biotinylated HCV IRES using lysates of 293FT cells expressing Flag-eIF2A (Δ462–501) with an internal deletion of the M domain. The amounts of input lysates and proteins loaded to control lanes are indicated in each panel