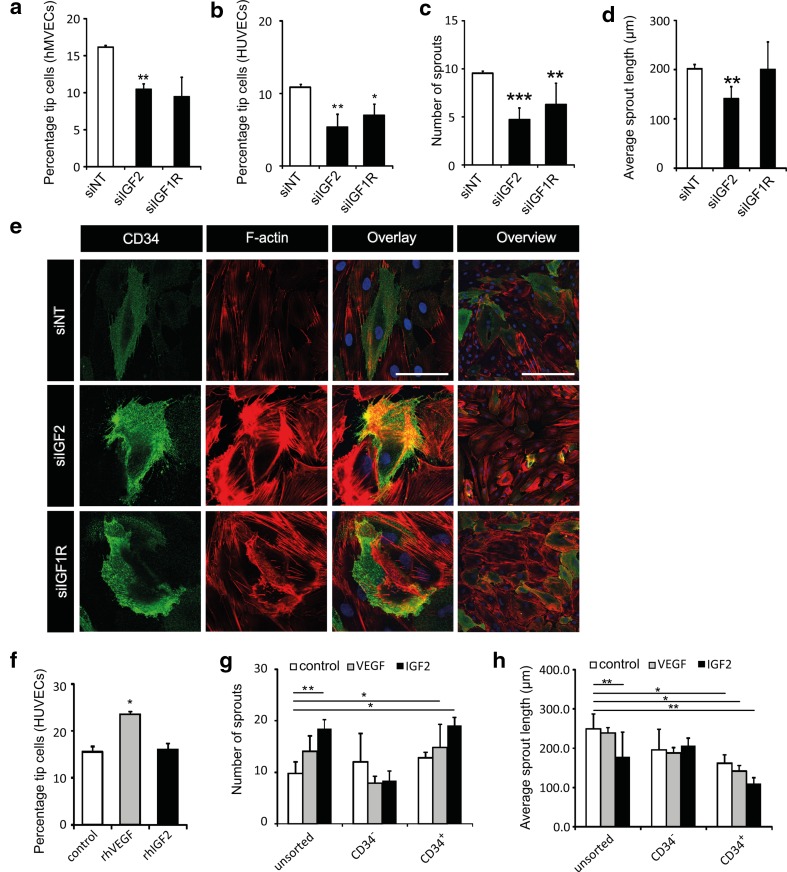
Fig. 3.
IGF2 and IGF1R are essential for CD34+ tip cell fate. a, b Effect of knockdown of IGF2 and IGF1R expression on percentages of CD34+ tip cells. Bars show percentages of CD34+ hMVECs (a) and HUVECs (b) treated with siNT, siIGF2, or siIGF1R as detected by flow cytometry. c, d Quantification of numbers of sprouts (c) and average sprout length (d) of spheroids composed of HUVECs after treatment with siNT, siIGF2, or siIGF1R. e Analysis of CD34+ tip cell morphology after knockdown of IGF2 and IGF1R expression. Staining of CD34 (green), F-actin (phalloidin, red), and nuclei (DAPI, blue) in hMVECs. Scale bars represent 50 µm (first 3 columns) and 100 µm (last column). f Effect of rhIGF2 on CD34+ HUVEC tip cell percentages. Bars shows CD34+ tip cells of HUVECs treated with either 25 ng/mL BSA, 25 ng/mL VEGF-A, or 50 ng/mL rhIGF2 as detected by flow cytometry. g, h Effects of VEGF and IGF2 on the number of sprouts (g) and average sprout length (h) in spheroids of CD34+ tip cells or CD34− non-tip cells. Data in a–d and f–h are shown as mean ± standard deviation after factor correction. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 as compared to control