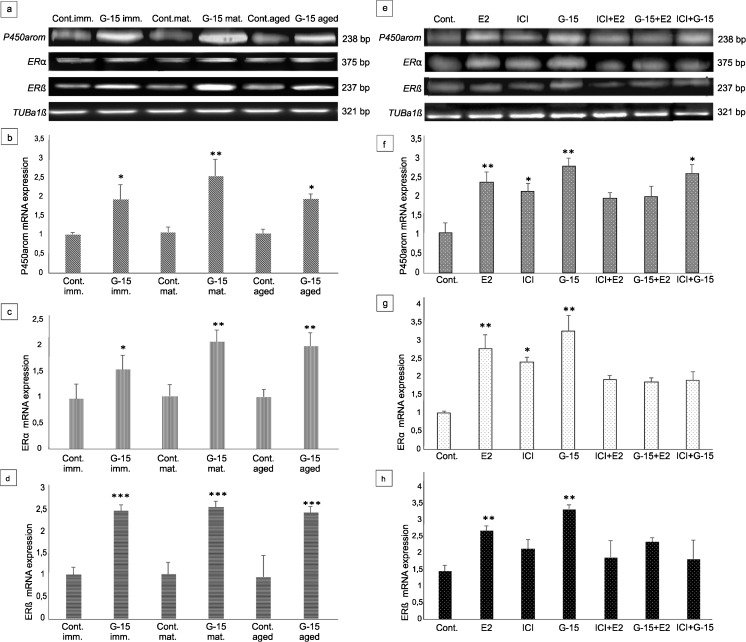
Fig. 7.
Effect of GPER blockage on mRNA expression of aromatase and estrogen receptors α and β in mouse testes and Leydig cells in vitro. (a, e) Representative gel electrophoresis of qualitative expression of P450aromatase, ERα, ERβ in mouse testes (immature, mature and aged) (a) and MA-10 Leydig cells (e). (b–d, f–h) Relative level (relative quantification; RQ) of mRNA for P450aromatase (b), ERα (c), ERβ (d) in mouse testes (b–d) and MA-10 Leydig cells (f–h), determined using real-time RT-PCR analysis 2 − ΔCt method. As an intrinsic control, the tubulin α1a mRNA level was measured in the samples [(a, e) -qualitative expression]. RQ is expressed as means ± SD. Asterisks show significant differences between control mice and those treated with G-15 (50 μg/kg bw) and control MA-10 Leydig cells and treated with G-15 (10 nM), ICI (ICI 182,780; 10 μM), E2 (17β-estradiol; 10 nM) alone and in combination for 24 h. Values are denoted as ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗ p < 0.001. From each animal, at least three samples were measured. Samples of cultured Leydig cells were measured in triplicate