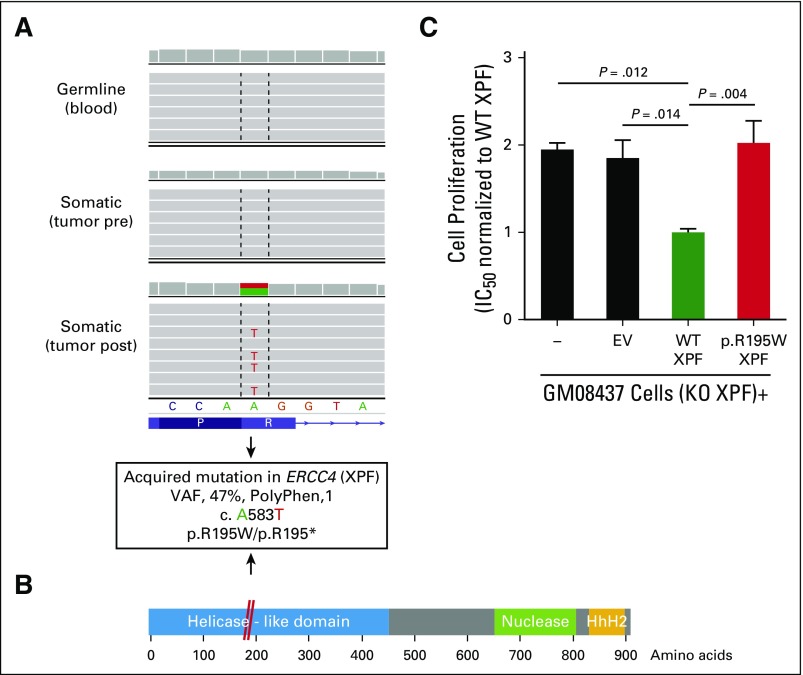
Fig 4.
Genomic and functional validation of an acquired mutation in ERCC4 (XPF) as a resistance mechanism to lurbinectedin. (A) Integrative genomics viewer plot shows mutation in ERCC4 identified by exome sequencing in patient 2. (B) Representation of XPF domains that shows the location of the p.R195W mutation (red). (C) Functional validation of the p.R195W mutation in XPF-deficient (XPF knockout [KO]) GM08437 cells complemented with empty vector (EV; control), wild-type (WT), or p.R195W XPF; the IC50 values of lurbinectedin normalized to the levels of XPF WT are shown. Data are mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments with three biologic replicates per group. HhH2, two consecutive helix-hairpin-helix motifs; PolyPhen, Polymorphism Phenotyping; post, postlurbinectedin; pre, prelurbinectedin; VAF, variant allele frequency.