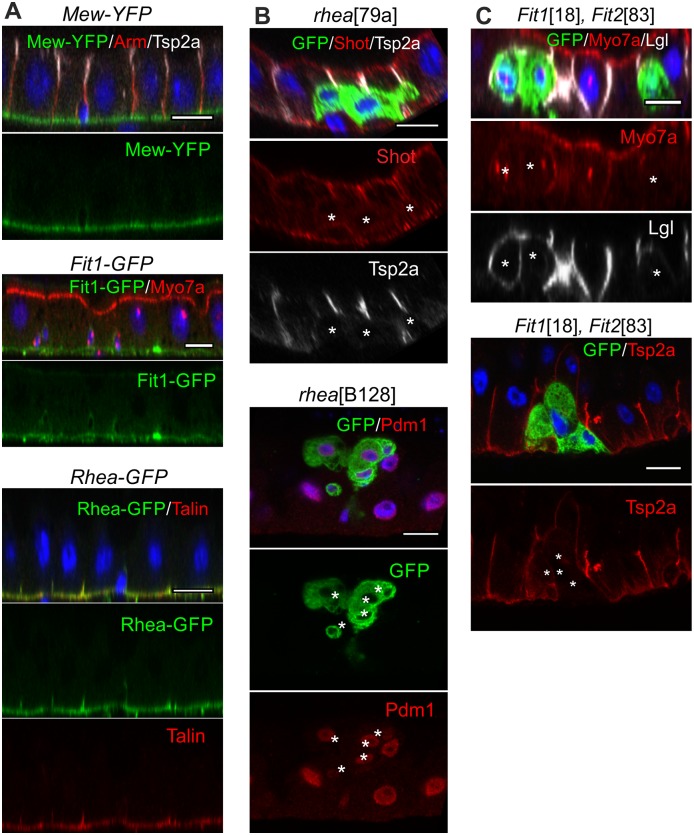
Fig 6. The integrin adhesion complex is required for EC polarisation and integration.
(A) The α-integrin Mew and the cytoplasmic adaptor proteins of the integrin adhesion complex, Talin (Rhea) and Fermitin (Fit, also known as Kindlin), localise to the basal surface of the midgut epithelium. Mew-YFP, Rhea-GFP (protein trap insertions), and Fit1-GFP (a genomic fosmid construct) [66] were detected with an anti-GFP antibody (green), whereas the subcellular localization of Talin was also revealed with an anti-Talin antibody (red). (B) rhea79a mutant cells (marked by GFP, green) detach from the basement membrane and fail to polarise. Shot (red) is apically enriched in neighbouring wild-type ECs but is not localised in rhea mutant cells, which fail to form SJs marked by Tsp2a (white). Most rheaB128 mutant cells (marked by GFP, green) express Pdm1 (red), a marker for differentiating ECs. (C) Fit118 Fit283 double mutant clones show a similar phenotype: Myo7a is not enriched apically (red), Lgl (white) spreads around the whole plasma membrane, and SJs fail to form as shown by the loss of Tsp2a localization (red). White asterisks * mark the mutant clones. Scale bars, 10 μm. EC, enterocyte; GFP, green fluorescent protein; Lgl, Lethal (2) giant larvae; Myo7a, Myosin 7a; SJ, septate junction; Tsp2a, Tetraspanin 2a; YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.