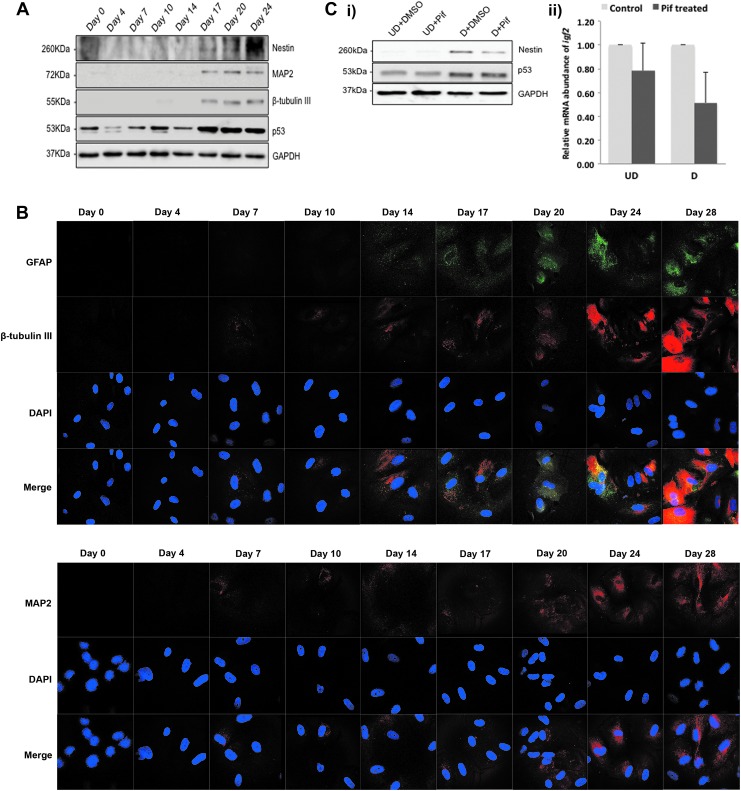
FIG. 3.
p53 is induced during neural differentiation in hAFS cells. (A) hAFS cells were cultured in differentiation medium for 4, 7, 10, 14, 17, 20, and 24 days. Abundance of p53, Nestin, MAP2, and β-tubulin III was monitored by western blotting. GAPDH was used for loading control. (B) hAFS cells were cultured on cover slips in differentiation medium for up to 28 days. At the indicated time points, cells were fixed and stained with antibodies for glial fibrillar acidic protein (green), β-tubulin III (red), and MAP2 (red). The cell nucleus was stained with DAPI (blue). (C) hAFS cells were cultured in duplicates for 9 days in differentiation medium containing retinoic acid (D) or left undifferentiated for control (UD). Where indicated, cells also received pifithrin-α (Pif; 10 μM f.c.) or the vehicle DMSO. One of the duplicates was used to monitor Nestin as a marker for neural differentiation and p53. GAPDH was used for loading control (i). From the second duplicate, RNA was prepared, transcribed into cDNA, and analyzed by qRT-PCR for expression of igf2. Abundance of igf2 mRNA was normalized by determining the abundance of the housekeeping gene β-actin. Relative abundance of igf2 mRNA in the cells with control siRNA was set to 1. The graph shows mean values and experimental variation of two independent experiments (ii). DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd