Fig. 3. Full scale, verbal and performance IQ distribution between cases with severe CHD and control subjects with no CHD within the 22q11.2DS population.
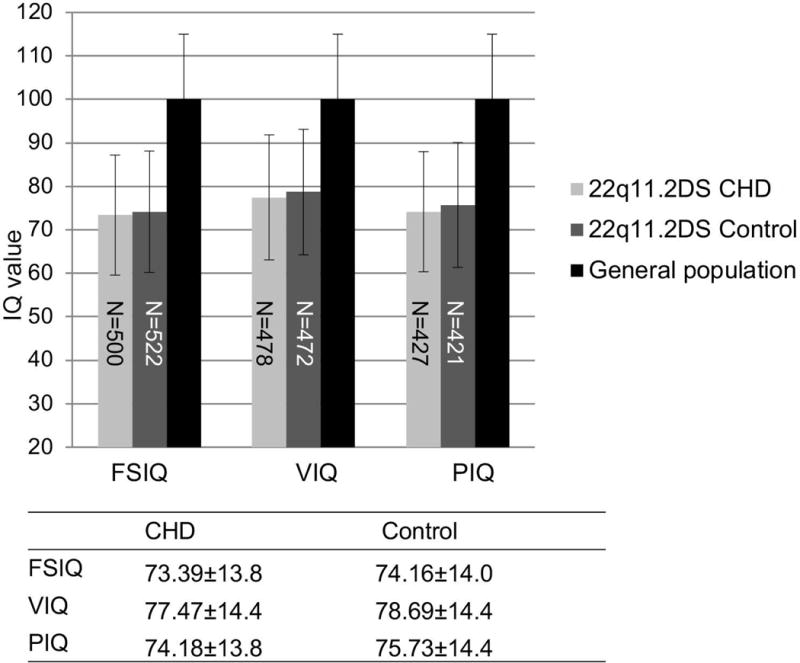
Severe CHD is defined as subjects with either tetralogy of Fallot, persistent truncus arteriosus or interrupted aortic arch type B. Control subjects for CHD cases had 22q11.2DS but no detectable heart or aortic arch defect. IQ values were expressed as mean±SD. An independent-samples t-test was conducted to compare IQ scores in subjects with the presence of severe CHD and controls within the 22q11.2DS cohort. All P values were > 0.05. Numbers in the bars denote the sample size of each category.
