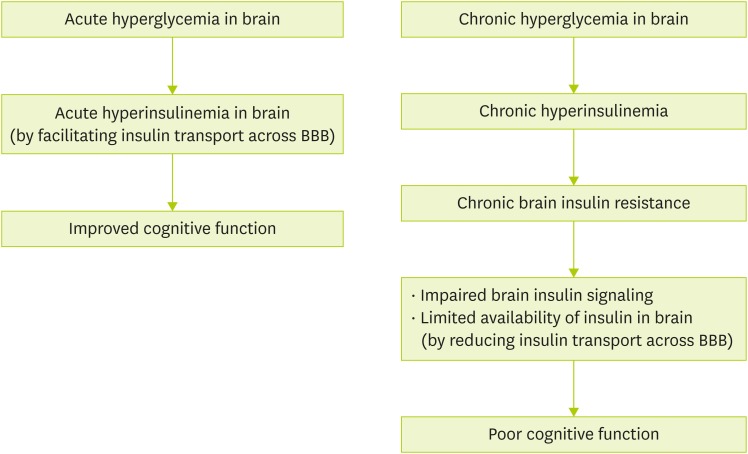
Figure 2. Acute/chronic hyperglycemia and cognitive function. Acute hyperglycemia facilitates insulin transport into brain resulting in acute hyperinsulinemia. Presence of high levels of insulin for a short time improves spatial and verbal memory. On the other hand, chronic exposure to high blood glucose in brain induces chronic brain insulin resistance. Uncontrolled brain insulin resistance accompanied with impaired brain insulin signaling and limited availability of insulin may cause poor cognitive function.
BBB, blood-brain barrier.