Figure 4. Effect of sleep stage and arousal on genioglossus AD duration following five‐breath CPAP drops during sleep.
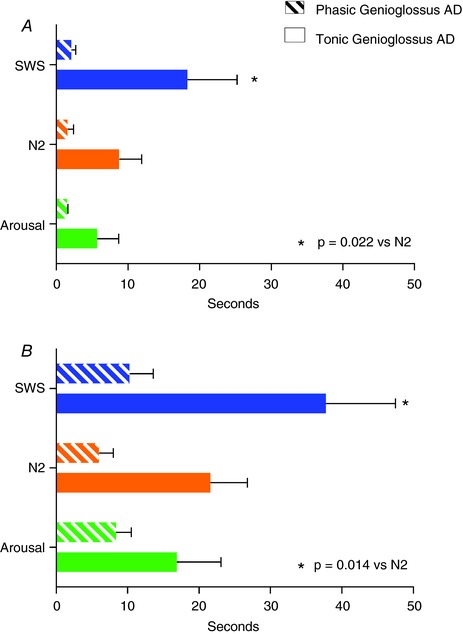
A, AD calculated from when the ventilatory drive was back to eupnoeic ventilation (pre‐CPAP drop levels). B, AD calculated starting from the end of the obstructive events. Tonic AD duration during SWS was twice the value compared to AD during N2 sleep (*). There was a trend for a shorter tonic AD duration when an arousal was present compared to without arousal (P = 0.08, values shown for NREM2). Phasic AD lasted a few seconds under all conditions, supporting the view that the respiratory activity of genioglossus muscle mimics the diaphragm activity and its duration is minimal after the ventilatory drive is back to the eupnoeic value. Data are based on mixed model analysis and represents group mean ± SEM; to promote normality, durations in seconds were transformed using Y = log10(time + 1) for analysis and then were back‐transformed for presentation. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
