Figure 1. Synaptic potentials invade distal axonal compartments.
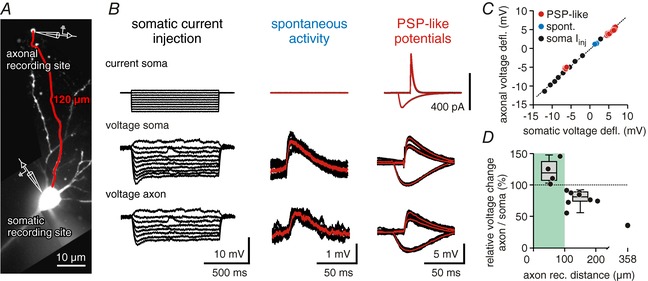
A, confocal image of a CA1 pyramidal cell used for dual soma/axon recordings (filled with Alexa 488). The axonal recording site was at a distance of 120 μm from the soma. B, somatic voltage deflections reach into distal axonal compartments. Traces show somatic current injection (top row), somatic voltage (middle row) and axonal voltage (bottom row). First column shows current/voltage relationships for somatic and axonal potentials, middle column shows spontaneous activity, and right column shows three postsynaptic‐potential like inputs induced by current injections to the soma (PSP‐like potentials). All traces were measured from the cell shown in A; average traces are shown in red. C, somatic vs. axonal voltage deflections for potentials shown in B. Hyperpolarizing and depolarizing potentials of different waveforms could be fitted with a linear function (dotted line). D, ratio of somatic to axonal voltage deflections vs. axonal recording distance. Within the first 100 μm, somatic potentials are amplified in the axon (median = +19.3%, left box plot; 4 cells). At soma–axon distances of 100–200 μm potentials in the axon retain ∼80% of the somatic amplitudes (median = −18.9%, right box plot; 8 cells).
