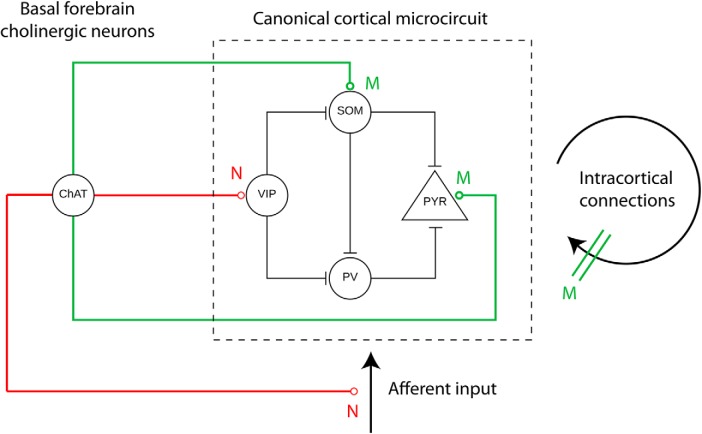
Figure 4.
Schematic drawing of cholinergic modulation of a cortical microcircuit. ChAT-positive cholinergic neurons in the BF modulate excitatory glutamatergic PYR cells and three types of inhibitory GABAergic interneurons, VIP-positive, SOM-positive, and PV-positive interneurons. Whereas PV and SOM neurons directly inhibit pyramidal neurons, VIP neurons inhibit SOM and PV neurons, resulting in disinhibition of pyramidal cell activity. Cholinergic modulation acts via nicotinic receptor (N, red) to enhance thalamic input and depolarize VIP neurons and via muscarinic (M, green) ACh receptors to depolarize pyramidal cells and PV and SOM interneurons and cause presynaptic inhibition at excitatory and inhibitory feedback synapses.