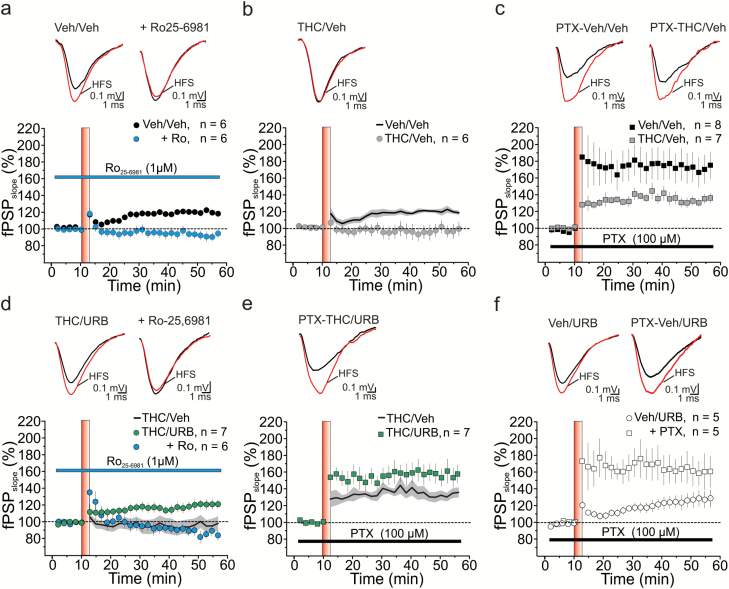
Figure 4.
Synaptic plasticity at MMP→DG connections. (A) Consistent with the expression of a newborn neuron-mediated form of LTP in the dentate gyrus (DG) of vehicle-treated (Veh/Veh) rats, high-frequency stimulation (HFS) of the medial perforant path (MPP) triggered a long-lasting potentiation of field post-synaptic potentials (fPSPs), which was abolished by the specific NR2B antagonist Ro26-6981 (1 μM); (RM2W, F1,10=21, P=.001; Veh/Veh vs Veh/Veh + Ro, P<.01). (B, C) Both newborn neuron-LTP (B, RM2W, F1,10=7, P=.02; Veh/Veh vs THC/Veh, P<.05) and LTP obtained in the presence of the GABAA blocker picrotoxin (PTX, 100 μM) (C, RM2W, F1,13=5, P=.04; Veh/Veh vs THC/Veh, P<.05) were impaired in THC-treated rats during adolescence. (D, E) URB597 administration fully rescued both Ro26-6981-sensitive LTP (D) and DGC LTP (E) in THC-treated rats (D, RM2W, F2,16=7, P=.008; THC/Veh vs THC/URB, P<.05; THC/URB vs THC/URB + Ro, P<.01; E, RM2W, F1,12=5, P=.04; THC/Veh vs THC/URB, P<.05). In contrast, URB597 treatment had no effect on these 2 forms of LTP recorded in the DG of Veh/Veh rats (Veh/URB, P<.05; Veh/URB+PTX, P<.05). (A–F) Time courses of normalized fPSP slopes (mean±SEM). Insets, averaged recordings (5 traces) before (black line) and after (red line) the delivery of high-frequency stimulation (HFS) protocol. HFS is indicated by the red vertical bar (B,D,E). Black lines (average fPSP slope) and gray areas (SEM) in B, D, and E show time courses from A, B, and C, respectively, and are reported here for comparison.