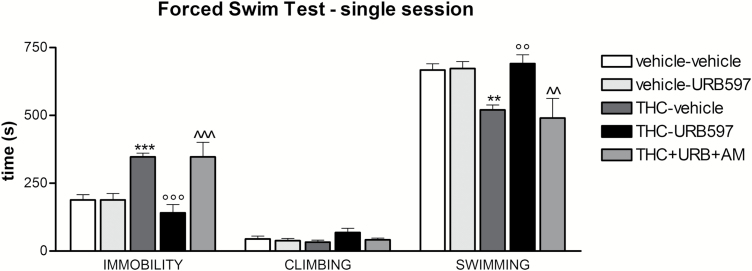
Figure 5.
Effect of co-administration of the CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 on URB597’s positive modulation of behavior in the forced swim test. Adolescent Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) administration significantly increased immobility and decreased swimming time during the 15-minute test session. Chronic URB597 normalized the time spent immobile and swimming when administered to THC-pretreated animals, however, co-administration of AM251 completely blocked the beneficial effect of URB597. Data are expressed as mean±SEM of n=5/10 rats/group and were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s posthoc test. **P<.01 and ***P<.001 vs vehicle; °°P<.01 and °°°P<.001 vs THC; ^^P<.01 and ^^^P<.001 vs THC + URB597.