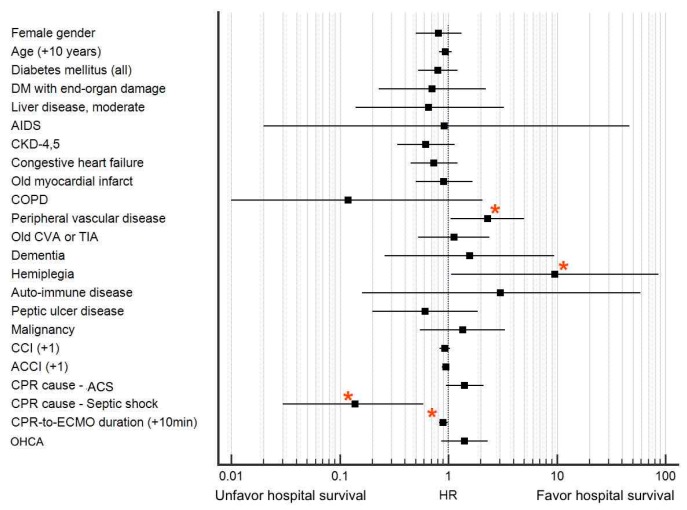
Figure 3.
Hazard ratio (HR) of individual factors for hospital survival. Four significant risk factors are marked with red asterisks, namely peripheral vascular disease (HR = 2.3, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.05–5.02, p = 0.037), hemiplegia (HR = 9.6, 95% CI = 1.06–86.8, p = 0.04), cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) due to septic shock (HR = 0.14, 95% CI = 0.03–0.59, p = 0.007), and CPR duration before extracorporeal membrane oxygenator (ECMO) run (CPR-to-ECMO duration) (HR = 0.9 for +10 min, 95% CI = 0.82–0.99, p = 0.04). Notably, age, Charlson comorbidity index (CCI), and age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity index (ACCI) were not significant risk factors (age: HR = 0.94 for +10 years, 95% CI = 0.82–1.07, p = 0.333; CCI: HR = 0.93, 95% CI = 0.83–1.04, p = 0.205; and ACCI: HR = 0.95, 95% CI = 0.87–1.02, p = 0.164). AIDS: acquired immune deficiency syndrome, CKD: chronic kidney disease, COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, CVA: cerebral vascular attack, TIA: transient ischemic attack, ACS: acute coronary syndrome, CPR-to-ECMO duration: CPR duration before ECMO run, OHCA: Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, DM: diabetes mellitus. * Denotes variables with p < 0.05 by univariate analysis.