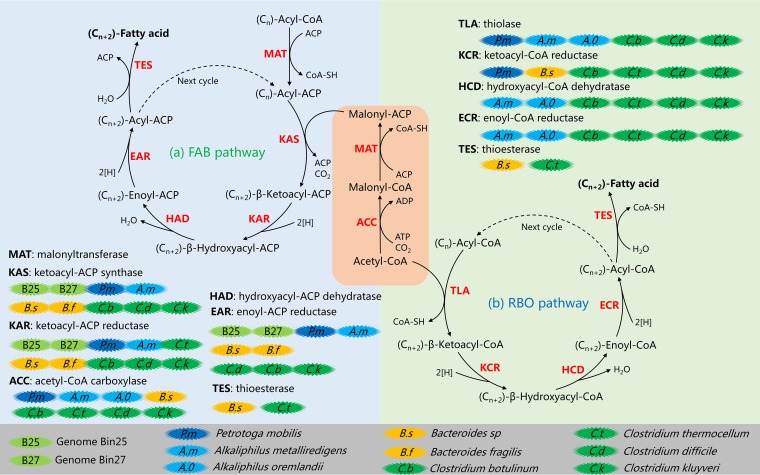
FIG 7.
Metabolic pathways and possible participants in chain elongation. The FAB pathway (top left) and RBO pathway (top right) are presented. The two pathways were constructed with information from enzymes annotated against the KO database. Abbreviations: ACP, acyl carrier protein; CoA, coenzyme A; 2[H], NADH/NADPH/ferredoxin. Dashed lines indicate the next cycle of elongation, of which (Cn+2)-acyl-CoA/ACP plays the role of starter molecule. Key enzymes are highlighted in red, and involved enzymes are listed in Table 3. (Cn), the number of carbon atoms of the molecule [for example, in (Cn)-acyl-CoA, an n of 1 means formyl-CoA, an n of 2 means acetyl-CoA, an n of 3 means propionyl-CoA, etc.]. Each turn of the cycle generates an acyl-CoA/ACP (indicated as Cn+2) which is two carbons longer than the initial acyl-CoA/ACP (indicated as Cn).