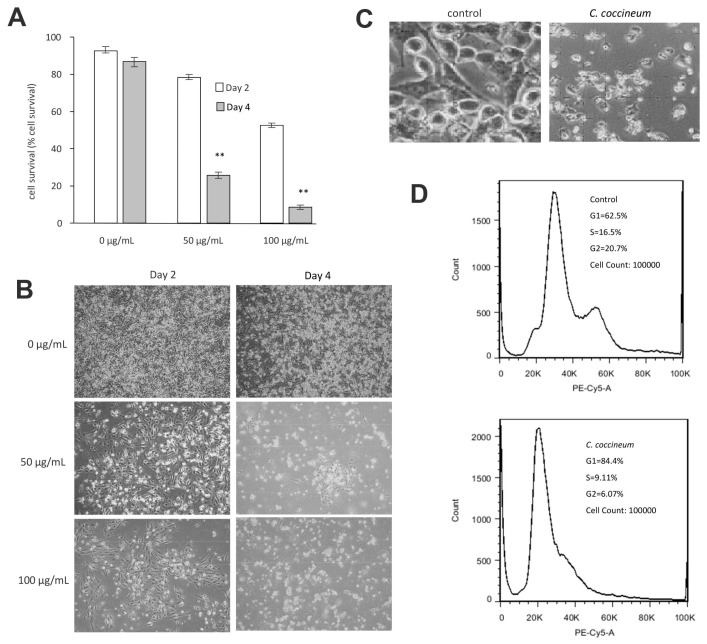
Figure 4.
C. coccineum decreases cancer cell viability: (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured in tissue culture plates to subconfluency in serum-free DMEM, to which the ethanol extract of C. coccineum was added at the concentrations as indicated. The cultures were maintained for 2 or 4 days. Addition of ethanol extract at the concentrations of 50 or 100 µg/mL significantly induced cell death as compared with the buffer control. (B) Typical photos showing detachment of cells from the plates treated with C. coccineum. (C) The extract of C. coccineum induced cancer cell fragmentation. (D) C. coccineum inhibits cancer cell cycle progression. We measured the cell cycle progression of the cells treated with the ethanol extract of C. coccineum (50 µg/mL). The treated cells had 84.4% of cells arrested in the G1 phase compared with un-treated cells having 62.5% in G1 phase. ** p < 0.01.