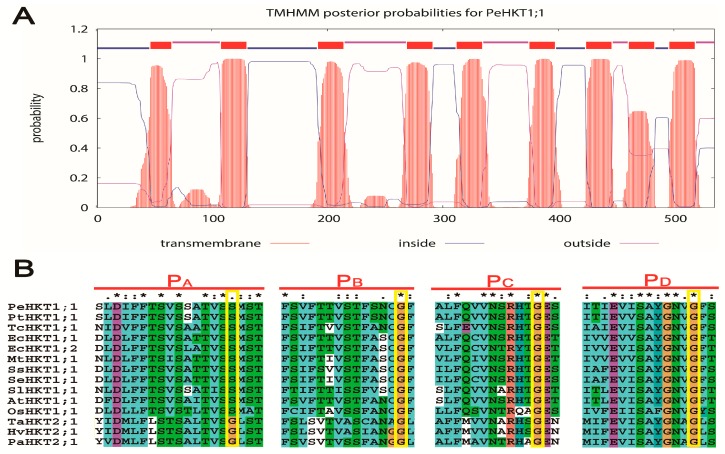
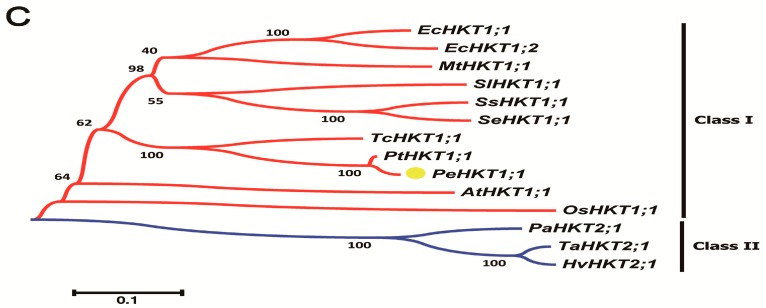
Figure 1.
The transmembrane helices, alignment, and phylogenetic tree analysis of HKT (high-affinity K+ transporter) amino acid sequences. (A) The transmembrane helices of PeHKT1;1 protein were predicted by TMHMN Server v.2.0. (B) The four conserved selectivity-filter-pore regions of HKT were aligned, and highlighted in yellow, using ClustalX 2.1 software. A line above the alignment was used to mark strongly conserved positions. Three characters (“*”, “:” and “.”) were used: “*” indicates positions which have a single, fully conserved residue. “:” and “.” indicates positions that have ‘strong’ and ‘weaker’ conserved residues, respectively. (C) Phylogenetic tree analysis of 14 HKTs from 12 different plant species by neighbor-joining method using MEGA v7.0 software with 1000 iterations bootstraps. HKT: high-affinity K+ transporter.