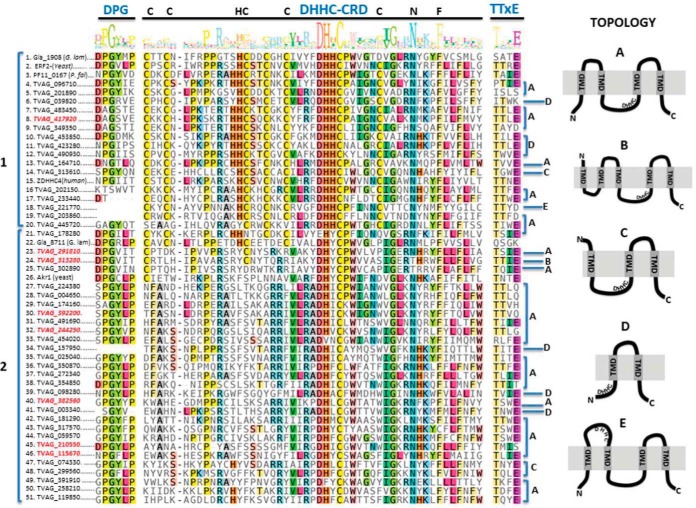
Fig. 2.
Sequence alignment and schematic drawing of T. vaginalis DHHC-containing proteins. Multiple sequence alignment of DHHC proteins shows conserved motifs. The amino acid sequences of the complete set of T. vaginalis DHHC, Giardia lamblia Gla_1908 (XP_001707652) and Gla_8711 (XP_001708375_Gla), yeast ERF2 (KZV09491_ERF2_SacC) and Akr1 (KZV12503_AKR1_SacC), P. falciparum PF11_0167 (001347838_PlaF) and human ZDHHC4 (CAG38542_ZDHHC4_Hum) were aligned using MAFFT (44). The conserved DHHC-CRD domain and the DPG and TTxE motifs are depicted in blue. DHHC proteins can be distinguished in two major groups (1 and 2). The group 1 encompasses proteins containing the tetrapeptide motif composed of DHHC as well as other conserved amino acids that form part of the DHHC-CRD (C-x2-C-x9-HC-x2-C-x4-DHHC-x5-C-x4-N-x3-F). The group 2 encloses proteins containing a variant of the classic DHHC where the second histidine of the tetrapeptide is generally replaced by a hydrophobic amino acid (Y, I, L, V, F, or M) and share other conserved amino acids that are absent in the classical PATs. IDs in red, DHHC proteins identified in the palmitoyl-proteome. A schematic representation of the five different topologies (A, B, C, D and E) found in T. vaginalis DHHC proteins is illustrated.