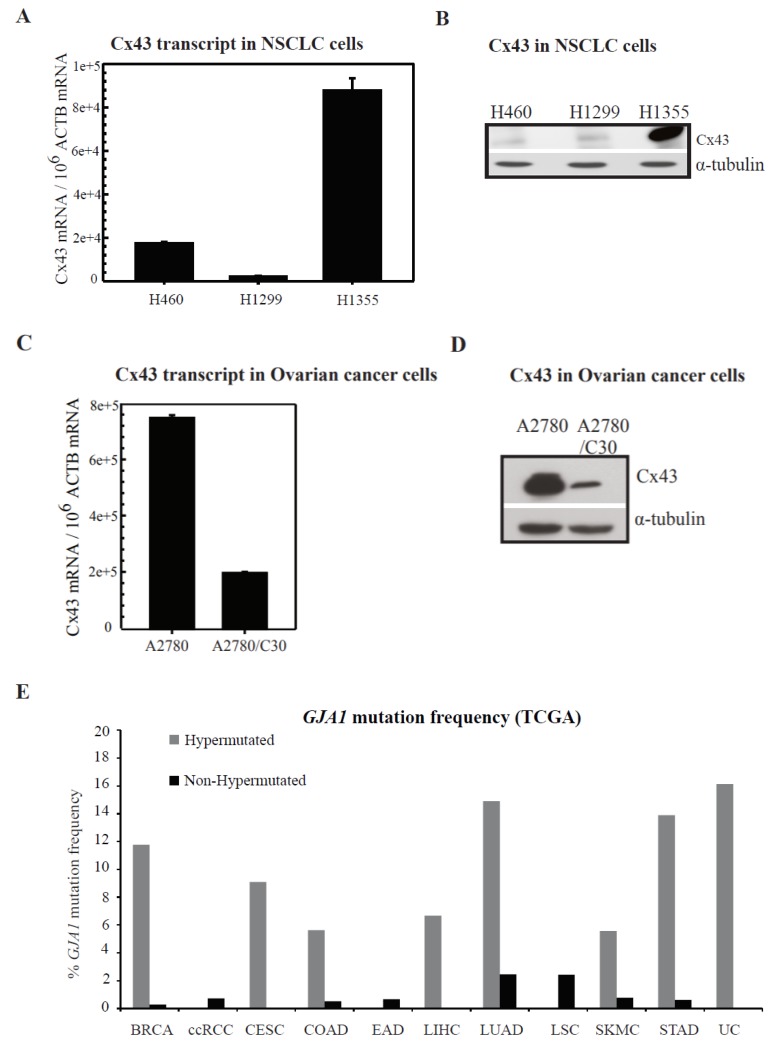
Figure 2.
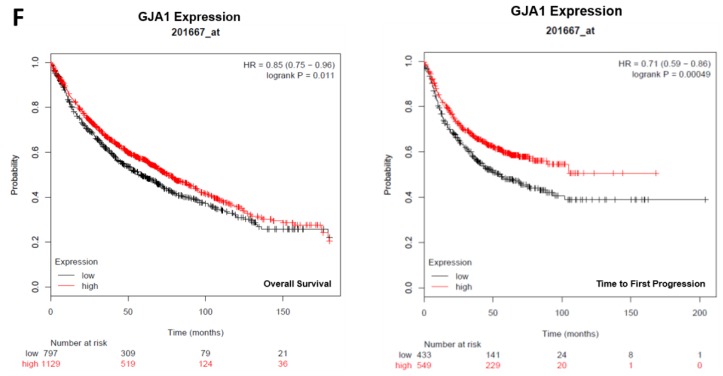
Cx43 in cancer. (A–D) Cx43 expression in NSCLC and ovarian cancer cells: RNA (A,C) and protein (B,D). (A,C) Total RNA was extracted from cells and analyzed using StaRT-PCR, as described in Section 4. Each PCR was run in triplicate. The transcript levels are represented as Cx43 mRNA/106 ACTB mRNA. The values are represented as mean ± SEM from triplicate PCRs. (B,D) Whole cell lysate from the cells were probed with antibody for Cx43 with α-tubulin as a loading control. Each PCR was run in triplicate. The transcript levels are represented as Cx43 mRNA/106 ACTB mRNA. The values are represented as mean ± SEM from triplicate PCRs. (E) Graph indicates the frequency of GJA1 somatic mutations in different cancers extracted from cancer studies in the TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) (data retrieval date November 23rd 2016). Cancer abbreviations are BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma; ccRCC, clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma; CESC, cervical squamous cell carcinoma; COAD, colorectal adenocarcinoma; LIHC, liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD, Lung Adenocarcinoma; LSC, Lung Squamous Carcinoma; SKMC, cutaneous melanoma; STAD, stomach adenocarcinoma; UC, uterine carcinoma. The graph has been divided to indicate mutation frequencies in hypermutated and non-hypermutated cancer. (F) Survival plots indicating probability of overall survival and time to first progression in lung cancers based upon GJA1 expression in human tumors obtained from kmplotter.org.