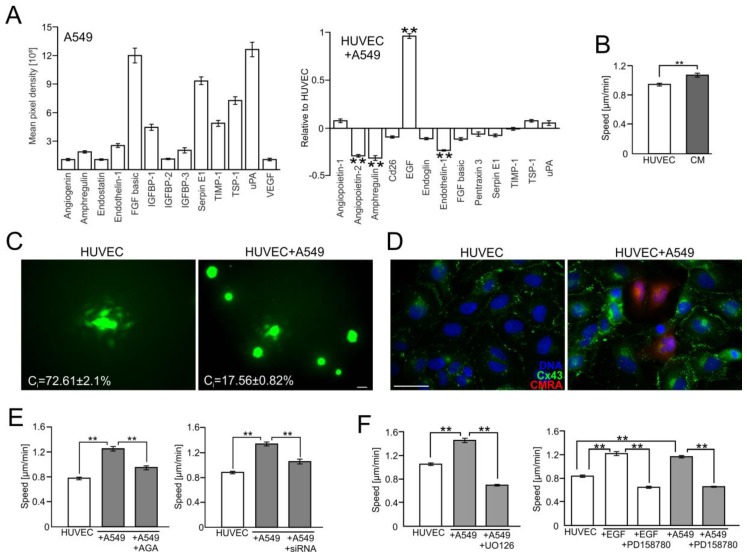
Figure 2.
A549 cells impair the endothelial barrier function via the activation of the Cx43/EGF/ERK1/2-dependent intercellular signaling axis. (A) A549 cells were seeded onto HUVEC monolayers as in Figure 1 and co-cultured for 24 h. Then, the expression of angioactive proteins was semi-quantitively estimated with an antibody array kit (see Materials and Methods). Plots show the densitometrically estimated dot intensities, illustrating the protein amounts in A549 cells (in a.u.; left) or in A549/HUVEC co-cultures relative to the HUVEC control. (B) A549-conditioned medium (3:5) was added to HUVECs and their motility was estimated with time-lapse videomicroscopy for 7 h. (C) Calcein-loaded HUVEC (left) or A549 cells (right) were seeded onto HUVEC monolayers and GJIC (coupling ratio-Ci) was estimated by a calcein transfer assay after 1 h. Concomitantly, Cx43 expression in HUVECs and in HUVEC/A549 co-cultures was estimated with immunofluorescence (D). (E) The effect of AGA (70 μM) and Cx43 silencing by siRNA on HUVEC motility. (F) HUVECs were cultured in the presence of EGF or A549/HUVEC co-cultures were established as above and the effects of EGFR- or ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD158780 and UO126, respectively) on HUVEC motility were estimated with time-lapse videomicroscopy. Error bars represent SEM. Scale bar = 40 μm. The statistical significance of the differences was tested with one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey’s HSD (B,E) or non-parametric Dunnett comparison (A,F); ** p < 0.01. All results are representative of at least three independent experiments (n ≥ 3). Note the presence of EGF in A549/HUVEC co-cultures and the attenuating effect of chemical Cx43/EGFR and ERK1/2 inhibition on A549-induced HUVEC activation.