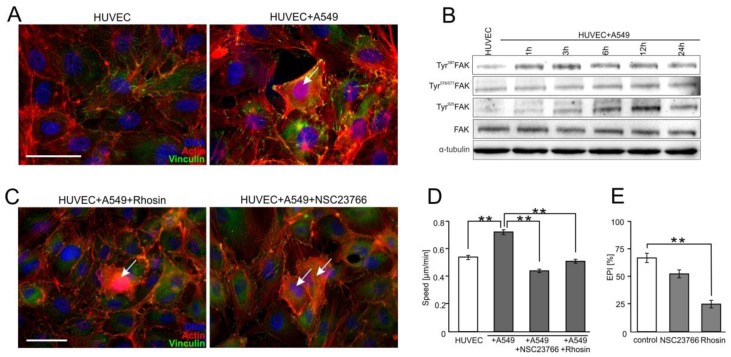
Figure 4.
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK)/RhoA-dependent signaling participates in the activation of HUVECs by A549 cells. (A) A549 cells (marked with arrow) were seeded onto the monolayer of HUVEC as described in Figure 1, cultivated for 6 h, fixed, and stained for F-actin and vinculin. (B) A549/HUVEC co-cultures were established as above, and Tyr397, Tyr576/577, and Tyr925 FAK were analyzed at the indicated time points by immunoblotting and quantified by densitometry (Figure S5D). (C) Cytoskeletal architecture of HUVEC cultured in co-cultures with A549 cells treated with Rhosin (left) or NSC23766 for 6 h (right). (D,E) A549/HUVEC co-cultures were treated with Rhosin and NSC23766 followed by the analyses of HUVEC motility (D) and A549 diapedesis ((E); 6 h). Error bars represent SEM. The statistical significance of the differences was tested with one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey’s HSD (D,E); ** p < 0.01. All results are representative of at least three independent experiments (n ≥ 3). Scale bar = 40 μm. Note that RhoA/Rac1-dependent disruption of endothelial continuum by A549 cells is accompanied by FAK activation and cytoskeletal rearrangements in proximal HUVECs.